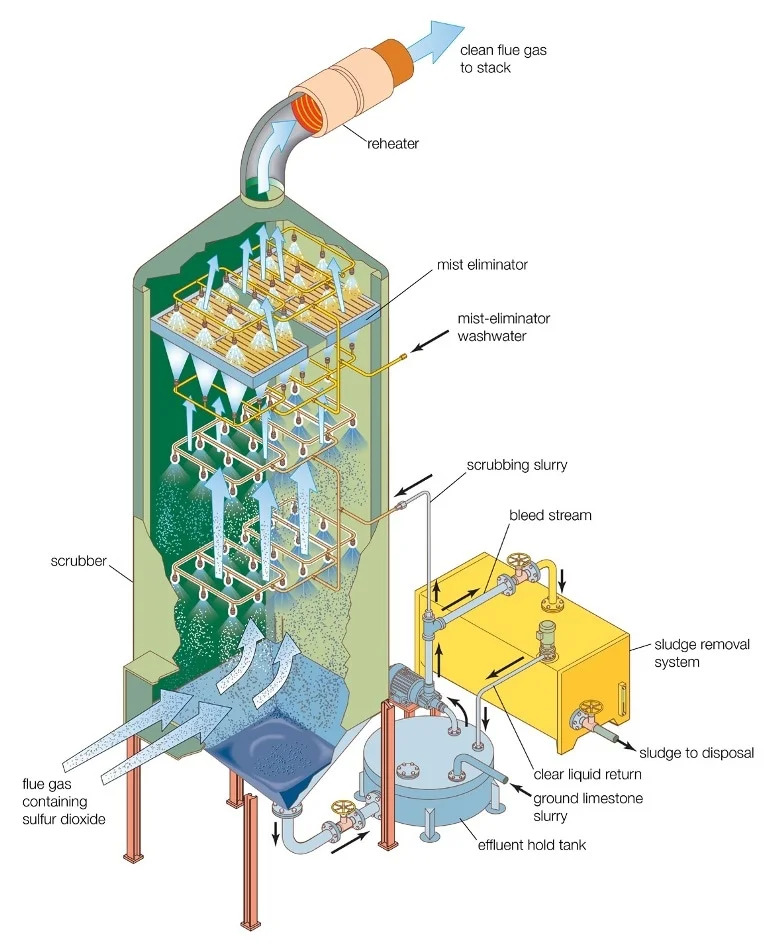
Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD) system
Why in news?
Environment Ministry has exempted most coal-fired power plants from the mandatory installation of FGD systems, reversing its 2015 directive due to factors like declining ambient sulphur dioxide (SO₂) levels, the naturally low sulphur content in Indian coal, high installation costs, and vendor constraints.
Key Features of FGD Systems
- FGD systems typically use alkaline reagents such as lime or limestone slurry, which react chemically with sulfur dioxide in the flue gas to convert it into neutral or solid compounds like calcium sulfate (gypsum).
- Most systems consist of a two-stage approach: first removing fly ash from the flue gas, then absorbing SO2 in a scrubber tower where the gas contacts the alkaline slurry.
- Wet limestone-based scrubbers are the most common, achieving around 90-97% removal efficiency of sulfur dioxide.
- Variants include wet scrubbers, spray dryer absorbers, and dry sorbent injection systems, each having different methods and efficiencies of emission control.
- FGD systems are essential for meeting environmental emission standards by significantly reducing SO2 which causes acid rain.
The revised regulation is based on expert committee recommendations and air quality survey findings, citing that Indian SO₂ emission levels are often well below the national standard, and the health impact of SO₂ is now considered less significant for PM2.5 than previously thought.
Download Pdf


Get in Touch