Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC)
Why in news?
- The GCC has approved a new "one-stop" travel system that will allow citizens to complete immigration, customs, and security checks at a single checkpoint before departure for intra-Gulf flights.
- This system, starting with a pilot phase between the UAE and Bahrain in December 2025, aims to reduce airport processing times and enhance regional integration, potentially expanding to all six member states (Saudi Arabia, Oman, Qatar, Kuwait, Bahrain, UAE).
- This initiative is modeled after the European Union's Schengen coordination and is part of a broader effort toward seamless travel and economic integration in the Gulf.
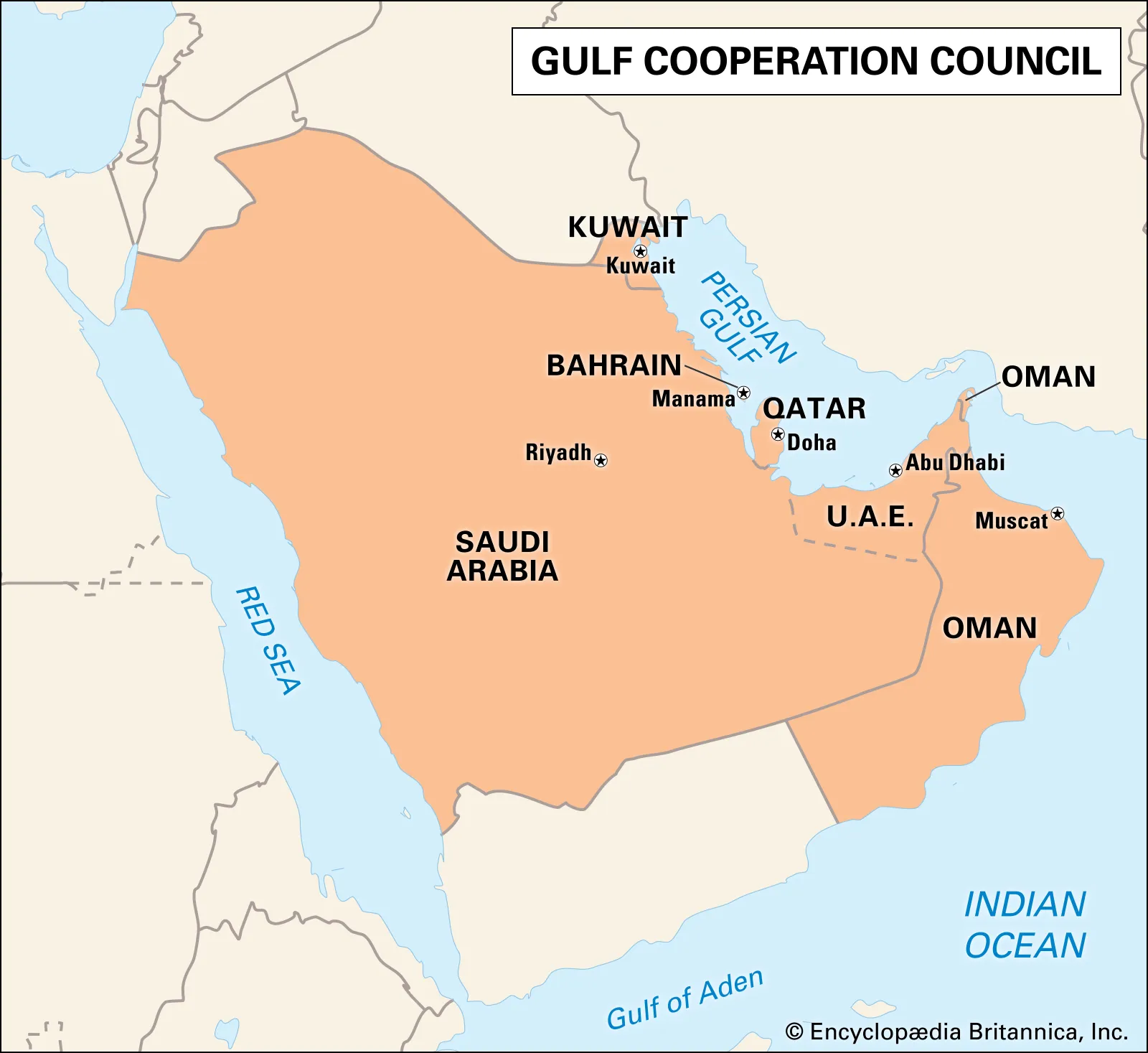
Key Facts about the GCC:
- Founded on May 25, 1981.
- Members: Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, UAE.
- Main objectives include coordination, integration, and cooperation across economic, social, and cultural fields.
- The GCC has pursued a common market, labor mobility, tax coordination, and professional certification interoperability.
- Maintains a defense planning council to coordinate military cooperation.
- The presidency of the council rotates annually.
Relevance of the GCC in 2025:
- The GCC remains strategically significant due to its role as a global energy hub, contributing majorly to oil and gas markets.
- It attracts strong foreign direct investment (FDI), supported by infrastructure projects, economic diversification efforts, and ambitious renewable energy goals.
- Despite regional geopolitical tensions, the council emphasizes regional integration, visa harmonization, and cross-border infrastructure as means to sustain competitiveness.
- GCC economies are projected to grow about 3% in 2025 and 4.1% in 2026, driven increasingly by non-oil sectors.
- GCC countries increasingly act as mediators in regional geopolitical conflicts, enhancing their diplomatic importance.
- India-GCC bilateral trade was around USD 178.56 billion in 2024-25, showing deep economic ties.
Download Pdf