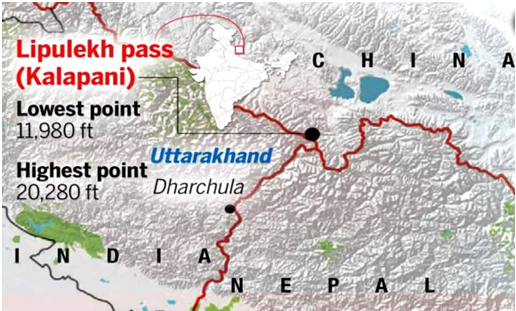
Lipulekh Pass
India and China agreed to resume border trade through Lipulekh Pass post-Covid-19, which Nepal objects to diplomatically.
The dispute impacts India-Nepal relations and involves diplomatic discussions, with China remaining neutral in the dispute.
Lipulekh Pass dispute
Location and Claims: Lipulekh Pass is located in Uttarakhand, India, near the tri-junction of India, Nepal, and China. Nepal claims that areas including Lipulekh, Kalapani, and Limpiyadhura belong to its territory, based on historical interpretation of the 1816 Treaty of Sugauli and its constitution. India administers these areas as part of Uttarakhand and rejects Nepal’s claims.
Treaty and Boundary Interpretation: The conflict hinges on the interpretation of the Kali River boundary set by the Treaty of Sugauli. Nepal asserts the river’s origin is at Limpiyadhura, placing disputed territories on their side. India states the river originates downstream near Lipulekh, thus including these territories within India.
Historical Context: India has controlled and administered Lipulekh, Kalapani, and the surrounding regions since the 1962 Sino-Indian War. India also opened the Lipulekh Pass for trade with China since 1954. Nepal’s formal territorial claims emerged later, especially intensifying after 2019 when India released a new political map showing these areas within Indian borders.
Strategic Importance: It serves as a gateway to the higher Himalayas and is strategically valuable for India in terms of security, troop mobility, and monitoring China along the Line of Actual Control (LAC). The pass provides a shorter trade route and access to Kailash Mansarovar in Tibet.
Download Pdf


Get in Touch
