What is strait of hormuz?
·
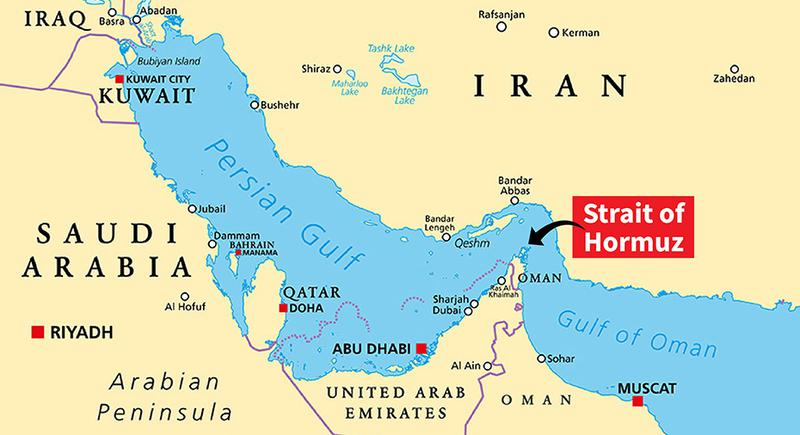
Strait of Hormuz – It is a critical narrow waterway between Iran and Oman, and connects the Persian Gulf with the Gulf of Oman and the Arabian Sea.
·
Narrow Path - It is just 33 km at its narrowest point, while the width of the shipping lane in the to and fro directions is only 3 km
- Strait of Hormuz is a critical narrow waterway between Iran and Oman. It connects the Persian Gulf with the Gulf of Oman and the Arabian Sea.
- It provides the only sea passage from the Persian Gulf to the open ocean and is one of the world’s most critical energy chokepoints. Around 20% of the global oil and gas supply- including shipments from Saudi Arabia, Iraq, the UAE, Qatar, and Iran- transit this narrow channel daily.
- If it is closed by Iran, oil prices could jump to over $120, or even $150 per barrel from $74 per barrel.
- At just 33 kilometers wide at its narrowest point, with shipping lanes only 3 kilometers wide in each direction, the strait is particularly vulnerable to disruption.
- Oil Transit Chokepoint - Around one-fifth of global liquid petroleum fuel consumption and global liquefied natural gas (LNG) trade transiting the strait.
- LNG Transit - Around one-fifth of global liquefied natural gas trade also transited the Strait of Hormuz in 2024, primarily from Qatar.
- Unique Route - Because of its geographic location, there is no sea route alternative to the Strait of Hormuz.
- Significance for India -Much of India’s oil from key West Asian suppliers like Iraq, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE reaches Indian ports via the Strait of Hormuz.
- A bulk of India’s LNG imports, which come predominantly from Qatar, also come through this vital choke point.
- Significance for Iran - Iran itself depends on the Strait of Hormuz for its trade, particularly oil exports to China, any blockade could impact Tehran considerably, experts pointed out.
- West Asian Oil&Energy Export – Almost all of the west Asian countries depends on this route to export their oils to rest of the world.
What are the potential impacts of closure of strait of hormuz on India?
Has the Strait ever been closed?
Despite past threats, Iran has never closed the Strait of Hormuz- even during major conflict- due to its global energy importance and the risk of strong retaliation from regional powers and the US. Iran might refrain from choking the Strait of Hormuz as:
·
Rupture Iran's relationship with Oman (which owns the southern half of the strait) and the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC States).
·
Heavily impact China, Iran’s largest trading partner. China is the number one importer of oil, accounting for nearly three-quarters of Iran’s oil export.
·
Impact Iran: Closure of its oil exporting terminal and associated economic hit would fuel popular discontent, which might impact both regime stability, and reformist tendencies for Iranian President.
Importance of the Strait of Hormuz for India:
· The Strait of Hormuz is vital for India due to its energy dependence in the region with most of this energy coming via the Strait of Hormuz.
- Strategic Energy Chokepoint: India’s oil supply is heavily reliant on the region, with around 40% of its crude oil imports and 54% of its liquefied natural gas (LNG) imports travelling through the Strait of Hormuz. Any threat or blockade increases freight and insurance costs (risk premium), raising the landed price of oil and gas in India.
- Global Price Surge Impact: Even without direct supply cuts, tensions cause global oil price spikes, which hurt India due to its heavy dependence on energy imports. This can affect India’s trade deficit, foreign exchange reserves, rupee stability, and inflation levels.
- Indirect Impact via China: Even if India does not import Iranian oil (due to US sanctions), any disruption in Iran’s supply to China will push Chinese demand to India’s suppliers, tightening global supply and raising prices.
- Disrupting Global Energy Market – West Asian region is a critical cog in the international oil and gas flows.
- Hence, the closure is bound to raise concerns globally, including in India, particularly with regard to oil and gas supply security, and could lead to a jump in energy prices.
- Increase in Shipping Cost - Shipping and insurance rates along the route have gone up notably due to higher geopolitical risk premium.
- Energy Crisis in India - India’s largest source of crude oil is Russia, followed by West Asian suppliers Iraq, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE and India also buys oil from other countries in the region like Kuwait, Qatar, and Oman.
- Nearly 47 % of crude oil imported by Indian refiners was likely to have been transported via the Strait of Hormuz.
- Closure of the hormuz rioute will affect energy transport from these regions.
- Impact of Increased Energy Cost - Apart from supply disruption for India, the surge in international energy prices due to any such blockade would hit India due to its heavy reliance on imported oil.
- Affecting Indian Economy – The oil price rise also has a bearing on the country’s trade deficit, foreign exchange reserves, the rupee’s exchange rate, and inflation rate, among others.
- Impact on Entire Economy - Any fluctuation in oil prices has a trickle-down effect on the prices of many other goods and commodities.
Download Pdf
