CA-22/11/2025
Interstellar Objects
Why in news?
- NASA recently released new images and data from various missions (like Mars Perseverance and the Lucy spacecraft) tracking 3I/ATLAS, confirming its interstellar origin and providing valuable details on its trajectory and structure.
- Radio signals and further analysis have confirmed 3I/ATLAS as a natural comet, settling debates around its true nature.
Meaning and Features
- An interstellar object refers to asteroids, comets, or similar small bodies that were once part of another star’s planetary system but became unbound, entering interstellar space.
- These objects are identified by their hyperbolic orbits and excess velocities that show they cannot have originated in the solar system.
- Unlike planets or stars, they do not orbit the Sun and typically pass through the solar system on erratic, fleeting paths.
- Their study helps astronomers understand planetary formation processes and galactic dynamics, revealing how stellar and planetary systems evolve.
Notable Examples
- Only three interstellar objects have been officially recorded passing through our solar system, each providing unique opportunities for scientific study:
- 1I/Oumuamua (2017): The first detected interstellar object, noted for its mysterious elongated shape and lack of a typical comet tail.
- 2I/Borisov (2019): The second, observed as a more traditional, active comet from deep space.
- 3I/ATLAS (2025): The most recent, a comet-like body whose age has been estimated at over 4.6 billion years, making a close approach to Earth in December 2025.
Pharmacogenomics
Why in news?
Pharmacogenomics is transforming medicine by replacing trial-and-error prescribing with precision drug prescriptions based on genetic information. This approach improves safety and effectiveness in drug therapy.
What is Pharmacogenomics?
- Pharmacogenomics combines pharmacology (the study of drugs) and genomics (the study of genes) to understand genetic variations that affect drug absorption, metabolism, efficacy, and toxicity.
- Helps in prescribing drug according to genetic profiles can help optimize dosing, avoid harmful side effects, and increase effectiveness, moving away from the traditional 'one-dose-fits-all' approach.
Mechanisms and Applications
- Genetic differences, especially in drug-metabolizing enzymes like those in the cytochrome P450 family (e.g., CYP2D6, CYP2C9), play a crucial role in how individuals process many medications.
- Pharmacogenomic testing is increasingly used in clinical practice for drugs in cardiology, cancer therapy, psychiatry, pain management, and more, guiding safer and more effective treatment decisions.
Benefits
- Reduces trial-and-error in prescribing by identifying patients who may benefit from certain medications or who are at risk of negative drug reactions.
- Improves drug efficacy, minimizes adverse effects, and can sometimes reduce polypharmacy by targeting therapies according to genetic information.
Pharmacogenomics is a key part of precision medicine, helping healthcare providers offer individually tailored treatments and paving the way for a future where genetic information routinely guides medical decisions.
Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM)
Why in news?
At COP30 held in Belém, Brazil, India and Japan emphasized how JCM helps countries work together to reduce carbon emissions and share the benefits of such projects.
About Joint Crediting Mechanism (JCM)
- The JCM is a bilateral initiative launched by the Government of Japan in 2013 to facilitate global greenhouse gas (GHG) emission reductions through cooperation with developing and other partner countries.
- The JCM promotes the diffusion of advanced low-carbon technologies, products, systems, and infrastructure, while supporting sustainable development in partner countries.
Key Features of JCM
- Bilateral Cooperation: The JCM is a government-to-government mechanism, with both countries jointly overseeing project selection, implementation, and credit allocation.
- Technology Transfer: The mechanism emphasizes the transfer of advanced low-carbon technologies, fostering innovation and capacity building in partner countries.
- Quantifiable Credits: Emission reductions are quantified and credited, providing a transparent and measurable way to track climate action.
- Sustainable Development: Projects under the JCM are designed to contribute to the sustainable development of partner countries, aligning climate action with broader development goals.
Significance of JCM
- Climate Action: It enables Japan to meet its international climate commitments by leveraging emission reductions achieved abroad.
- Technology Transfer: It promotes the adoption of advanced low-carbon technologies in developing countries, accelerating their transition to sustainable development.
- Bilateral Relations: The mechanism strengthens bilateral ties between Japan and partner countries, fostering cooperation on climate change and sustainable development.
Japan has signed JCM agreements with 31 countries, including India, Indonesia, Vietnam, Bangladesh, and Ethiopia. These partnerships have led to the implementation of numerous projects in sectors such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and waste management.
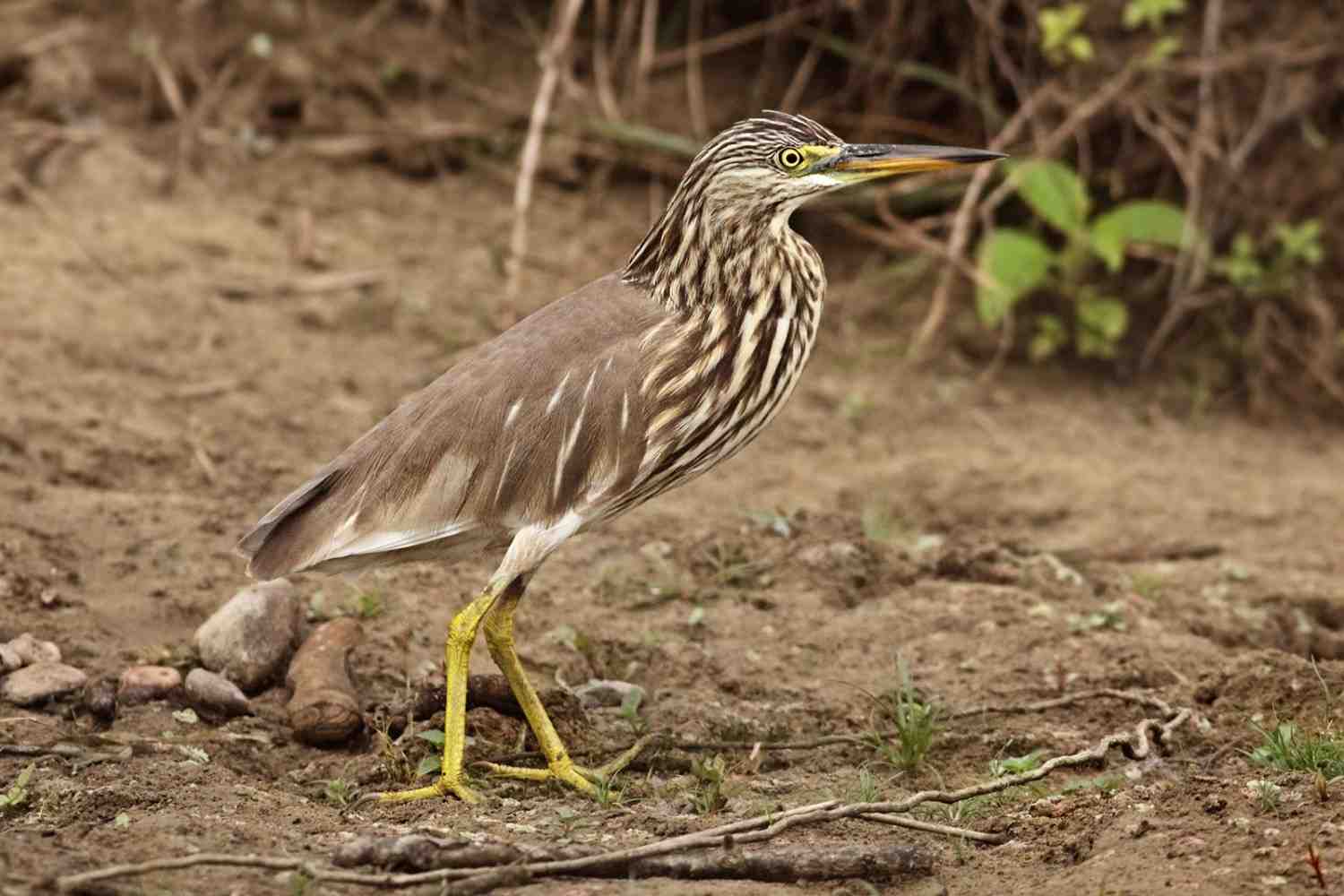
Why in news?
- Recent citizen-science data from Visakhapatnam suggests that Indian Pond Herons, along with cattle egrets, may be undertaking regular seasonal journeys along the East coast of India.
- This new evidence revives a 30-year-old mystery about their migratory patterns, particularly data previously collected from Chennai.
About
- Also known as the paddybird or Ardeola grayii
- Widely distributed across the Indian subcontinent, including southern Iran, Pakistan, India, Myanmar, Bangladesh, and surrounding islands.
- Identifiable by its brownish buff and streaked plumage on the head and neck
- It is usually around 45 cm in length.
- Classified as Least Concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
Doctrine of Clean Hands
Why in news?
The Division Bench of the Delhi High Court ruled that the principle of “clean hands” cannot be invoked to deny relief to a petitioner who has successfully proven cruelty, especially if the counter-allegations against them are unsubstantiated.
Key Features of the Doctrine
- Equitable Principle: The doctrine applies only to equitable remedies, not to claims for damages at law.
- Subject Matter Specific: The misconduct must be directly related to the matter in dispute. A party's unrelated wrongdoing does not automatically bar relief.
- Affirmative Defense: The doctrine is typically raised as an affirmative defense by the opposing party.
- Judicial Discretion: Courts have discretion in applying the doctrine, considering the nature and gravity of the misconduct and its impact on the fairness of the proceedings.
Application in Indian Jurisprudence
- In India, the Supreme Court and various High Courts have consistently emphasized the importance of the clean hands doctrine.
- The courts have held that litigants must approach the court with full transparency and integrity, disclosing all material facts relevant to the case.
- If a party has concealed facts, engaged in fraud, or acted in bad faith, the court may refuse to grant relief, even if the party has a technically valid claim.
- The doctrine is often invoked in cases involving fraud, concealment, or abuse of process.
Recent Delhi High Court judgment on the Doctrine of Clean Hands
- The case involved a divorce petition under the Hindu Marriage Act where the petitioner claimed cruelty by the spouse.
- The Family Court had dismissed the petition citing the petitioner’s unclean hands, relying on counter-allegations that were unsubstantiated.
- The Delhi High Court held that the doctrine of clean hands cannot be used to deny relief if the petitioner has proven cruelty and the counter-allegations are not established.
- The court emphasized that the doctrine prevents benefiting from one’s own wrongdoing but should not bar legitimate relief where statutory grounds like cruelty are proven with evidence.
Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI)
Why in news?
During India Maritime Week 2025, IWAI signed MoUs worth around ?3,000 crore with multiple partners including Assam Petro-Chemicals Ltd. and the Government of Assam, focusing on strengthening Assam’s inland water transport network and logistics ecosystem.
Key facts about the Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI)
- Established on October 27, 1986, under the Inland Waterways Authority of India Act, 1985.
- Functions under the Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways.
- Responsible for development, regulation, and maintenance of national inland waterways.
- Headquarters located in Noida, Uttar Pradesh, with regional offices across India.
- Manages 111 national waterways for shipping and navigation.
- Develops infrastructure like terminals, jetties, and navigational aids.
- Promotes cargo and passenger movement via inland waterways to reduce logistics costs.
- Supports river cruise tourism and regional connectivity projects, especially in the Northeast.
Significance for Northeastern region
- Geographical Connectivity: The Northeast is characterized by challenging terrain with hills, mountains, and dense forests, making road and rail connectivity difficult and expensive. Inland waterways offer a natural and efficient alternative for transport through rivers, reducing dependency on difficult land routes.
- Economic Development: Improved water transport infrastructure under IWAI facilitates trade and commerce by lowering transportation costs for goods and raw materials. This boosts local economies and helps integrate the Northeast with the rest of India and neighboring countries.
- Resource-Rich Region: The region has abundant natural resources and agro-based products. Efficient waterways can enable easier movement of these products to markets domestically and for export, enhancing livelihoods and economic opportunities.
- Tourism Potential: Northeast India is known for its scenic rivers and cultural heritage. IWAI’s initiatives to develop waterways for passenger transport and river cruises can boost tourism, generating employment and cultural exchange.
- Strategic Importance: Given the Northeast’s international borders with several countries, improving inland water transport supports strategic and defense logistics, besides promoting regional cooperation and connectivity within the Act East policy framework.
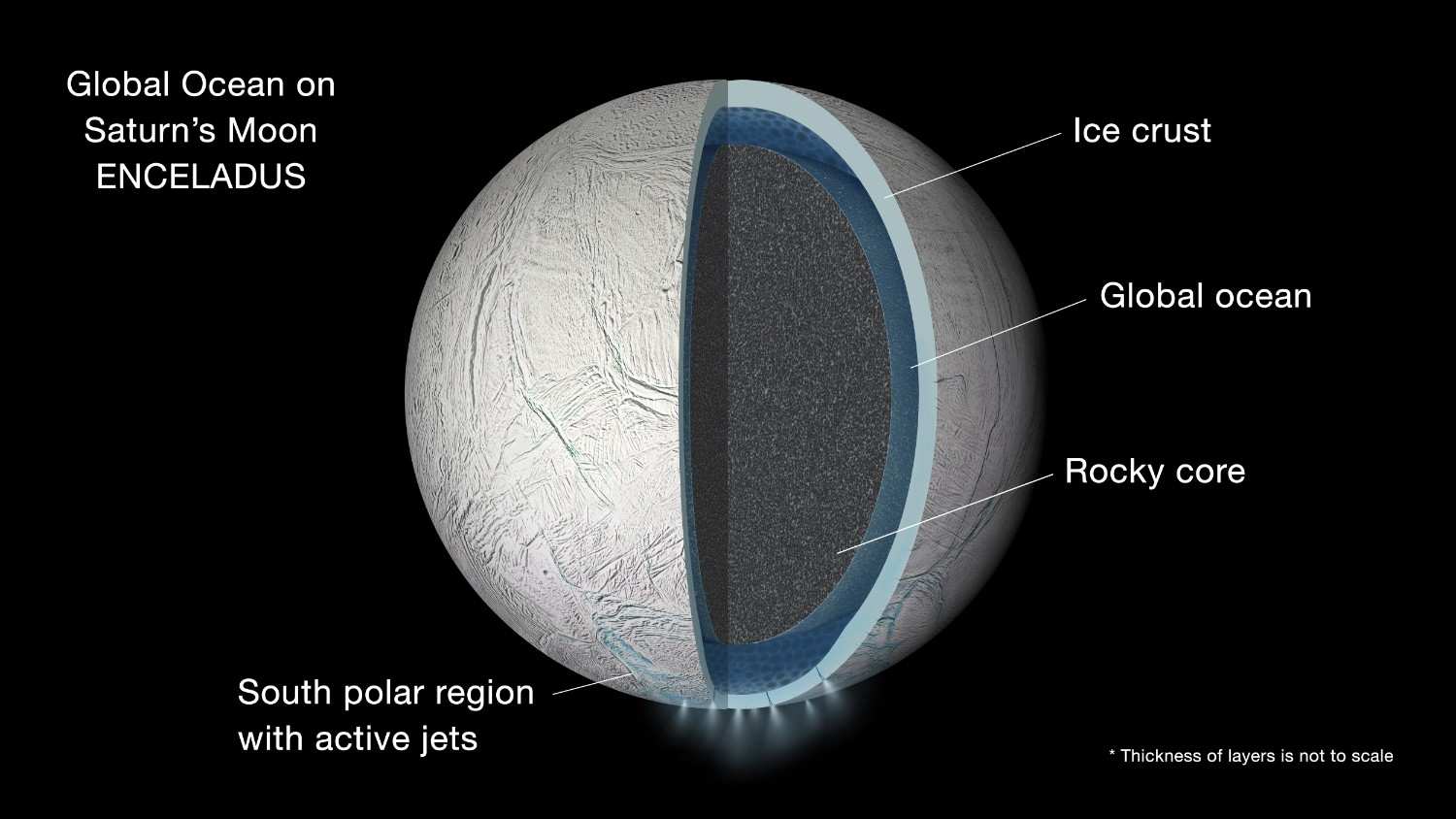
About Enceladus
- It was discovered in 1789 by William Herschel.
- Sixth largest moon of Saturn
- Diameter: About 500 kilometers (310 miles), making it the sixth-largest moon of Saturn.
- Surface: Highly reflective icy surface with fresh snow deposits hundreds of meters thick.
- Orbit: Located within Saturn's E Ring and orbits in a nearly circular path and is tidally locked, meaning the same face always points toward Saturn.
- Subsurface Ocean: Has a global saltwater ocean beneath an ice shell estimated 30-40 km thick.
- Geological Activity: Active geyser-like plumes eject water vapor, ice particles, organic compounds, and molecular hydrogen from fissures near its south pole.
Recent discoveries
- NASA's Cassini mission data revealed fresh, complex organic molecules from Enceladus' subsurface ocean, including aliphatic, cyclic ester, and ether families, indicating active organic chemistry that could support biochemical processes.
- Evidence suggests Enceladus' ocean has remained stable over geological timescales, a crucial factor for the potential development and persistence of life.
- Cosmic rays may drive radiation-based chemistry within Enceladus’ ocean, providing a possible energy source for life in subsurface environments beyond sunlight.
- The mass and composition of Enceladus' plume ejecta have been re-evaluated, showing more material expelled than previously estimated.
- Hydrothermal activity on the ocean floor is confirmed to create mineral-rich water interactions, analogous to Earth's deep-sea vents, which could sustain microbial ecosystems.
- ESA and NASA prioritize planning future missions to further explore Enceladus by sampling its plumes and potentially landing near the south pole to analyze ocean chemistry in situ.
New models help explain the moon's internal heat generation and ice shell dynamics, crucial for understanding its habitability potential.
Colombo Security Conclave (CSC)
Why in news?
Seychelles has officially become the sixth full member of the Colombo Security Conclave during the 7th National Security Adviser (NSA)-level meeting held in New Delhi on November 20, 2025.
About Colombo Security Conclave
- The Colombo Security Conclave (CSC) is a regional security grouping formed to promote closer cooperation among member states on critical security issues and to enhance regional security in the Indian Ocean Region.
- Initially known as the Trilateral for Maritime Security Cooperation, it started in 2011 among India, Maldives, and Sri Lanka.
- Over time, it expanded to include Mauritius (2022), Bangladesh (2024), and Seychelles as an observer state. Malaysia has also participated as a guest.
The CSC focuses on cooperation under five key pillars
- Maritime Safety and Security
- Countering Terrorism and Radicalization
- Combating Trafficking and Transnational Organized Crime
- Cybersecurity and Protection of Critical Infrastructure and Technology
- Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief
This expansion underscores CSC's growing importance as a platform for regional trust-building, joint exercises, information sharing, and capacity building to address emerging security challenges in the Indian Ocean Region.
Bhoramdev Wildlife Sanctuary
Why in news?
- In November 2025, poachers killed two bison in the Chilfi East Range of the sanctuary, raising concerns about wildlife protection measures.
- The sanctuary is also close to being declared a Tiger Reserve. This move, supported by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) and Union Ministry. Once approved, it will play a key role in the Kanha-Achanakmar corridor, important for tiger conservation and movement.
Key facts about Bhoramdev Wildlife Sanctuary
- Location: Kabirdham (Kawardha) district, Chhattisgarh, India.
- Year of Notification: 2001.
- Area: Approximately 352 sq.km.
- Landscape: Part of Maikal range, Satpura hills; vital role in Kanha–Achanakmar tiger corridor.
- Connects Kanha National Park (Madhya Pradesh) with Achanakmar Wildlife Sanctuary (Chhattisgarh).
- Flora: Predominantly Sal, Saaj, Tendu, and Eucalyptus.
- Fauna: Includes Bengal tiger, leopard, sloth bear, sambar, gaur, wild boar, and diverse birds.
- Cultural significance: Home to tribal communities (Baiga, Gond, Kanwar) and the famed Bhoramdeo Temple.
- Eco-sensitive zone: Notified in 2025 with new conservation measures.
National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA)
- It is a statutory body under the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change,
- Established in December 2005 under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 (amended in 2006) to strengthen tiger conservation in India.
- It provides statutory authority to Project Tiger, ensuring legal compliance with its directives,
- Fosters accountability between the central and state governments for better management of tiger reserves.
- The NTCA oversees tiger conservation efforts, approves tiger conservation plans prepared by state governments.
- Ensures no alteration or de-notification of tiger reserves without its approval and that of the National Board for Wildlife.
Why in news?
The recent exercise, Sagar Kavach-02/25, was conducted along the Maharashtra & Goa coastline from November 19-20, 2025, with over 6,000 personnel and more than 115 sea and air assets participating.
About
- Exercise Sagar Kavach is a coastal security exercise conducted by the Indian Coast Guard to enhance the security of India's coastline against asymmetric threats.
- It involves coordinated participation from the Indian Coast Guard, Indian Navy, State Police, Marine Police, Customs, Fisheries departments, and other central and state agencies.
- The exercise simulates scenarios such as hijacking attempts, infiltration, smuggling, and terrorist threats to coastal infrastructure.
- It is conducted biannually at various locations along the Indian coastline, including Maharashtra, Goa, West Bengal, Gujarat, Andaman & Nicobar Islands, and others.
- Exercise Sagar Kavach strengthens the multi-layered Coastal Security Network and inter-agency coordination to safeguard maritime borders effectively.
The exercise fosters readiness for various real-time coastal security threats and ensures synergy between multiple maritime and law enforcement agencies.
Four new labour codes
Why in news?
- The four new labour codes came into force on November 21, reforming 29 existing labour laws to provide minimum wage guarantees, social security for about 400 million workers, enhanced worker safety, equal wages, and better compliance mechanisms.
New labour codes
- Code on Wages, 2019: Ensures statutory minimum wages and timely payment for all workers, extending wage protections broadly.
- Industrial Relations Code, 2020: Regulates hiring, firing, dispute resolution, and trade unions with faster dispute resolution and enhanced flexibility.
- Code on Social Security, 2020: Expands social security coverage including to gig and platform workers, formalizing benefits such as Provident Fund, Employees’ State Insurance, and insurance schemes.
- Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions Code, 2020: Prescribes national safety standards, workplace health and welfare measures including free annual health check-ups for workers above 40, and regulates working hours.
Need for New Labour Codes
- Outdated labour laws were fragmented, complex, and based on colonial-era frameworks, hindering adaptation to modern economic realities.
- Existing regulations created uncertainty and increased compliance burden for both workers and industries.
- Changing forms of employment (gig, platform, contract, and migrant work) required updated legal protections.
- There was a need to simplify labour governance and expand social security coverage universally.
- The codes aim to empower workers and enterprises for a resilient, competitive, and self-reliant nation.
Key Changes in Labour Codes
- Consolidation of 29 laws into 4 codes for wages, industrial relations, social security, and occupational safety.
- Fixed-term employees now receive equal benefits and gratuity after 1 year (reduced from 5 years).
- Women allowed to work night shifts with mandatory safety measures and written consent.
- Formal recognition and social security coverage extended to gig, platform, contract, and migrant workers.
- Mandatory appointment letters and statutory minimum wages applicable to all workers.
- Introduction of national floor wage and gender-neutral pay provisions.
- Simplified compliance through single registration, licensing, and returns.
- Enhanced workplace safety, including CCTV, safe transport, and security arrangements.
- Digital and media sector workers included under welfare benefits and mandatory appointment letters.
Benefits of New Labour Codes
- Workers gain formal employment recognition with benefits like timely wages, social security, gratuity, health coverage, and leave entitlements.
- Enhanced social security net with portability of benefits across states and sectors.
- Equal pay and protections for women, including anti-discrimination measures for transgender persons.
- Improved protections and welfare for fixed-term, contract, gig, and platform workers.
- Employers benefit from streamlined regulatory framework reducing compliance costs and enhancing ease of doing business.
- Strengthened dispute resolution with faster mechanisms and fewer redundant licenses.
- The reforms are pro-worker, pro-women, pro-youth, and promote employment growth, skill development, and industrial flexibility.
The new labour codes modernize India's labour laws, improve worker protections and benefits, extend social security universally, and simplify regulatory processes for employers, aligned with contemporary work environments and economic demands.
Post-AR6
About
- The "Post-AR6" refers to developments and updates following the release of the IPCC Sixth Assessment Report (AR6), completed in 2023.
- AR6 offered the most comprehensive, current scientific assessment of climate change including physical science, impacts, adaptation, vulnerability, and mitigation strategies.
Key insights and updates
- India and other regions facing intensified climate risks require region-specific, data-driven adaptation strategies to strengthen resilience in agriculture, cities, and public health systems.
- Observed climate changes continue, including warming trends, changes in monsoon rainfall, glacier mass loss acceleration in the Himalayas, and projections of further temperature rise and extreme weather events.
- Global and regional models under CMIP6 projects warming scenarios including risks of exceeding hottest recorded temperatures and large uncertainties in ocean productivity.
- 2023 synthesis report highlights the urgent need for deep, rapid greenhouse gas emission reductions to limit warming to 1.5°C, requiring emissions to peak by 2025, with about 43% reduction by 2030 relative to 2019.
- Despite commitments, current emissions pledges fall short of required emission cuts to meet the 1.5°C target.
- New funding arrangements for loss and damage due to climate impacts were agreed at COP27 as part of global climate negotiations following from AR6 findings.
Post-AR6 research papers are providing updated regional assessments on observed and projected climate changes, emphasizing adaptive responses to escalating compound climate risks.
Download Pdf