CA-21/11/2025
National Industrial Classification system (NIC)-2025
Why in news?
- NIC-2025 is the latest revision of the National Industrial Classification system released by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) in November 2025.
- It is designed to systematically categorize all economic activities in India for statistical and policy purposes. NIC-2025 replaces the earlier NIC-2008 classification.
Key Features of NIC-2025
- NIC-2025 shifts to a 6-digit coding structure, improving detail and flexibility compared to the 5-digit NIC-2008 system.
- It is aligned with the United Nations’ International Standard Industrial Classification of All Economic Activities (ISIC Revision 5), ensuring global comparability.
- The revision reflects emerging sectors, such as fintech, e-commerce, renewable energy, digital platforms, and blockchain, and recognizes indigenous sectors like Ayush healthcare and the handloom industry.
- There is expanded coverage of environmental activities, including carbon capture, waste management, and green economy initiatives, enhancing alignment with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- New classes have been created to better represent intermediation roles in retail, logistics, power, healthcare, and education.
- Technology-agnostic categories ensure activities are listed by nature, not production techniques (traditional vs modern).
Importance and Purpose
- The purpose of NIC-2025 is to provide a detailed, standardized classification system that facilitates accurate data collection, analysis, and reporting of economic activities.
- It supports government surveys, economic censuses, industrial registration, and policy-making by providing reliable sectoral data.
- It enhances the accuracy of sectoral data, boosts evidence-based policymaking, and supports global data reporting standards.
- The system is crucial for industry registration (MCA), business statistics, and priority sector lending by RBI.
Why in news?
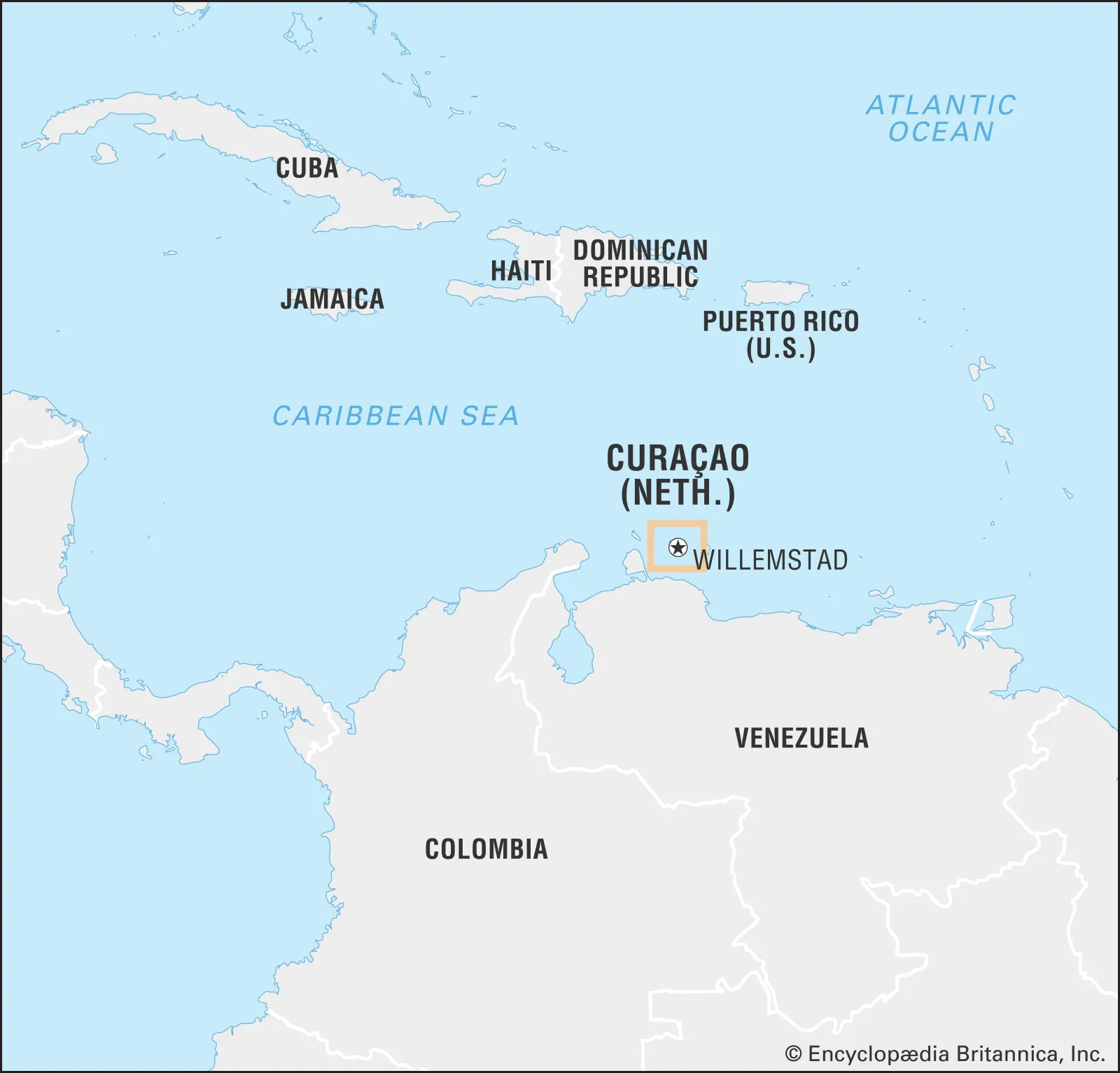
Curaçao makes history as smallest nation by population to qualify for a 2026 FIFA World Cup, making it the smallest nation by population ever to reach the tournament.
About Curaçao
- Curaçao is a Caribbean island country and a constituent country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands.
- It is located in the southern Caribbean Sea, about 60 km north of the coast of Venezuela.
- Its capital is Willemstad, known for its colorful Dutch colonial architecture and designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- The island has a population of approximately 156,000 to 165,000 people (2025 estimate).
- Economically, Curaçao has a high-income economy focusing on petroleum refining, tourism, banking, and exports such as the famous Curaçao liqueur and pharmaceutical aloes.
- Curaçao's historical role as a trade hub under Dutch West India Company control and its status as home to one of the oldest Jewish communities in the Western Hemisphere.
Why in news?
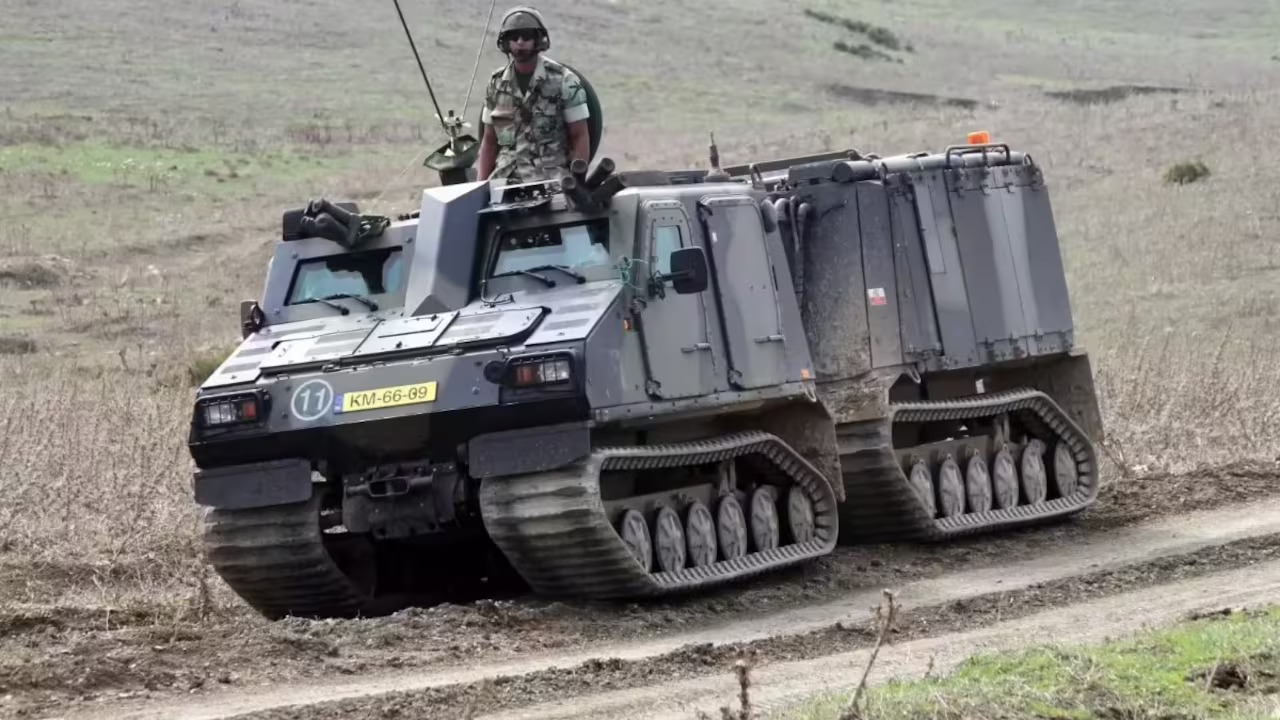
- The Indian Army has officially selected the BvS10 Sindhu as its new all-terrain tracked vehicle, with orders placed for 18 vehicles to be delivered over the next two years.
- This acquisition is part of a broader initiative to modernize and enhance operational readiness in challenging terrains such as the Himalayas, deserts, and marshlands.
Key facts about the BvS10 Sindhu armored all-terrain vehicle
- BvS10 Sindhu is a variant of the BvS10 articulated allterrain tracked carrier, adapted specifically for Indian conditions and inducted as a new mobility platform for the Indian Army.
- The name “Sindhu” is the designation chosen for the Indian variant, distinguishing it from other BvS10 versions in service with European users.
- It is manufactured in India by Larsen & Toubro under a technology transfer and partnership with BAE Systems Hägglunds, supporting India’s “Make in India” initiative.
- The initial contract includes the supply of 18 vehicles over two years, along with maintenance and life cycle support.
- The BvS10 Sindhu has low ground pressure tracks for excellent traction and the ability to traverse snow, mud, and water obstacles effectively.
- This vehicle will enhance the Indian Army’s capability for rapid troop movement and logistics in difficult terrains where traditional vehicles struggle.
- It marks the first adoption of the BvS10 platform in Asia, customized for Indian climatic and geographical conditions.
BIRSA 101
Why in news?
BIRSA 101 is India's first indigenous CRISPR-based gene therapy developed to treat Sickle Cell Disease (SCD). Named after the tribal leader Birsa Munda on his 150th birth anniversary.
Key features of BIRSA 101
- Developed by the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research - Institute of Genomics and Integrative Biology (CSIR-IGIB) and transferred to Serum Institute of India for scalable production.
- Uses the CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing tool, specifically a guided Cas protein (enFnCas9) that precisely corrects the single-nucleotide mutation in the HBB gene responsible for the disease.
- Delivered as a one-time infusion, aiming to enable the patient's body to produce normal red blood cells instead of sickle-shaped ones.
- Priced significantly lower than global CRISPR therapies to ensure accessibility to poorer populations.
- Designed to contribute to the vision of a "Sickle-Cell-Free Nation" by 2047, particularly benefiting underserved tribal populations in central and eastern India.
Sickle Cell Disease
- Sickle Cell Disease itself is a genetic blood disorder causing red blood cells to become rigid and sickle-shaped, leading to anemia, pain crises, infections, and organ damage.
- The disease is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, and carriers can unknowingly spread the defective gene.
BIRSA 101 marks India's entry into advanced gene therapies, leveraging CRISPR technology for precise, efficient, and cost-effective genome editing, positioning India as a global leader in this advanced medical field.
YUVA AI for ALL Initiative
About
- The YUVA AI for ALL Initiative is a free, national online course launched by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) under the IndiaAI Mission.
- It is designed to make Artificial Intelligence (AI) accessible and understandable to every Indian, especially the youth,
- Aiming to empower 1 crore (10 million) citizens with foundational AI skills.
- The course is self-paced with a duration of 4.5 hours and covers six engaging modules.
- It explain what AI is, how it works, AI's impact on education, jobs, creativity, the importance of ethical and responsible AI usage.
Key features of the initiative
- The course is free, practical, and uses simple language with real-life Indian examples.
- It is available on multiple platforms such as FutureSkills Prime, iGOT Karmayogi, and other popular ed-tech portals.
- Learners can complete the course at their own pace anytime, anywhere.
- Everyone who completes the course receives an official certificate from the Government of India.
- The course is meant for students, professionals, educators, and anyone interested in AI.
- It aims to bridge the AI knowledge gap, promote ethical AI use, and prepare India's workforce for AI-driven future job markets.
This initiative is part of the broader IndiaAI Mission launched by MeitY and Nasscom in 2023 that focuses on making AI work for India by encouraging domestic AI development and ensuring AI benefits different sectors in the country.
Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI) 2026
Why in news?
- India has fallen 13 places to rank 23rd in the Climate Change Performance Index (CCPI) 2026, moving from the “high” to the “medium” performance category, mainly due to continued coal dependence and the absence of a clear coal phase?out timeline.
Key facts about CCPI 2026
- CCPI 2026 assesses 63 countries plus the EU covering over 90% of global greenhouse gas emissions, on their climate mitigation efforts.
- The CCPI annual ranking is based on four main categories with 14 specific indicators:
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions (40% weight)
- Renewable Energy (20% weight)
- Energy Use (20% weight)
- Climate Policy (20% weight)
- Category ratings of India: medium in GHG emissions, climate policy, and energy use, and low in renewable energy, reflecting concerns about implementation speed and land/social conflicts around projects.
- No country is rated “very high” overall, so the top three positions remain vacant; Denmark is the highest?ranked country at 4th, followed by the United Kingdom and Morocco in 5th and 6th.
- The CCPI is published jointly by Germanwatch, the NewClimate Institute, and CAN International since 2005.
It highlights progress and gaps, showing that while global per capita emissions are falling and renewable energy is growing, the pace is still insufficient to meet global climate goals.
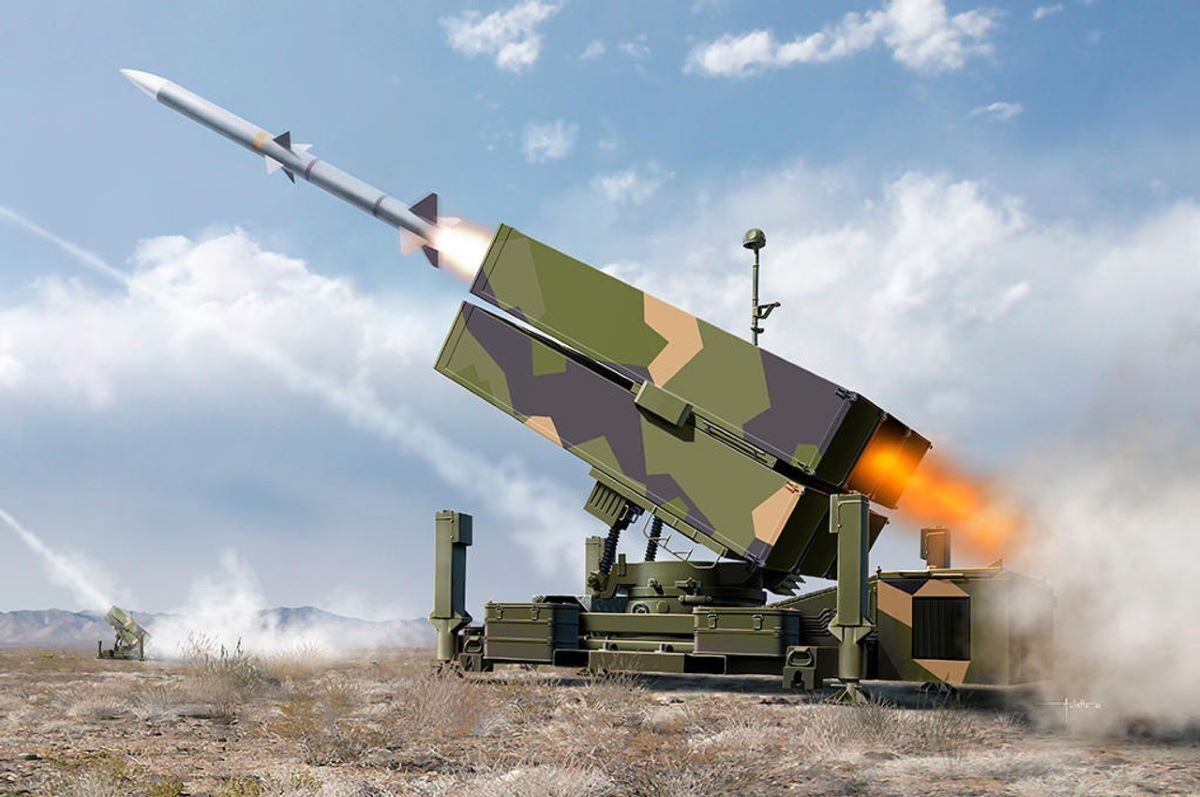
NASAMS (National Advanced Surface-to-Air Missile System)
Why in news?
NASAMS is a highly adaptable, networked short- to medium-range ground-based air defense system developed jointly by Norway's Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace and the U.S. company Raytheon (RTX Corporation).
Key Features
- It uses a network-centric architecture for enhanced survivability and integration with other air defense equipment and systems.
- The system's primary radar is a high-resolution 3D X-band phased array radar capable of 360-degree coverage with a detection range of about 75 kilometers.
- NASAMS can engage multiple targets simultaneously—up to 72 targets in active and passive modes—and is capable of firing missiles based on data from external sensors.
- The main interceptor missile used is the AIM-120 AMRAAM (Advanced Medium-Range Air-to-Air Missile)
- NASAMS 3, the latest upgrade, also incorporates AIM-9X Sidewinder missiles for shorter-range engagements.
- Launchers typically carry up to six missiles each.
Its networked design allows it to defend high-value assets, critical infrastructure, and population centers against a range of aerial threats including drones, cruise missiles, helicopters, and fixed-wing aircraft.
Why in news?
The volcano erupted recently on November 19, 2025, with a powerful eruption that sent ash clouds up to 13 kilometers high and pyroclastic flows that traveled down its southern slopes for up to 7 kilometers.
About Semeru volcano
- Semeru is the highest mountain on the Indonesian island of Java and one of Indonesia's most active volcanoes, located in East Java province.
- It stands at 3,676 meters (12,060 feet) above sea level and is part of the Tengger Volcanic Complex.
- Semeru is a stratovolcano also known as Mahameru, meaning "The Great Mountain" in Sanskrit.
- It has a long history of frequent eruptions, with at least 61 eruptive periods recorded since 1818, many involving lava flows and pyroclastic density currents.
Causes of Semeru eruption
- The 2025 eruption of Mount Semeru was caused by the collapse of the lava dome at its summit, which was destabilized by monsoon rains.
- This dome collapse triggered a series of pyroclastic flows (fast-moving avalanches of hot gas, ash, and volcanic rock) that traveled down the mountain's slopes.
- The buildup of volcanic material in the summit area over the past few years reached an unstable threshold, and the heavy rains likely acted as a trigger for the collapse, causing the eruption to occur.
Historically, Semeru eruptions have been significant and destructive; for example, the 2021 eruption caused fatalities and displacement, highlighting the volcano's potential hazards. Its continuous activity since 1967 makes it one of the most persistently erupting volcanoes globally.
Global Methane Status Report 2025
Why in news?
The Global Methane Status Report 2025, released by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and the Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC) at COP30.
Key highlights of report
- Global methane emissions reached about 352 million tonnes in 2020 and may increase to around 369 million tonnes by 2030 under current policies.
- Methane is a powerful greenhouse gas, roughly 80 times more potent than Cover 20 years, responsible for about one-third of current warming.
- Agriculture is the largest methane source (42%), followed by energy (38%) and waste (20%).
- India is the third-largest emitter globally, contributing 9% of methane emissions, mainly from agriculture.
- The Global Methane Pledge (GMP), signed by 159 countries covering 57% of emissions, aims to cut methane emissions 30% by 2030 from 2020 levels.
- Full implementation of mitigation measures in G20+ countries (holding 72% of reduction potential) could prevent over 180,000 premature deaths, reduce crop losses by 19 million tonnes, and deliver economic benefits exceeding $330 billion annually.
- Without stronger methane controls, emissions could rise by 21% by 2050, exacerbating climate change, health risks, and food insecurity.
Way forward
- Enhancing methane emission monitoring, reporting, and verification systems to improve data accuracy and accountability.
- Promoting adoption of best practices and technologies for methane reduction, such as leak detection and repair in oil and gas, improved livestock management, and organic waste diversion.
- Strengthening international cooperation and financing mechanisms to support developing countries in methane mitigation efforts.
- Highlighting co-benefits of methane reduction beyond climate, including significant health improvements, lower crop losses, and economic opportunities.
National Policy for Organ Transplantation
Why in news?
The Supreme Court of India has directed the Centre to frame a uniform National Policy for Organ Transplantation to address wide disparities and inconsistencies across states in organ donation and allocation.
Directions by Supreme Court
- Establish State Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisations (SOTOs) in all states, including those lacking them (e.g., Manipur, Nagaland).
- Evolve model allocation criteria to prevent gender- and caste-based discrimination.
- Amend birth and death registration forms to include brain death certification and organ donation offer status.
- Provide guidelines to protect live organ donors from exploitation and ensure their post-donation care.
Objectives
- Create an equitable, transparent, and efficient organ transplantation system.
- Ensure fair access to organ transplantation irrespective of gender, caste, or state.
- Prevent exploitation of live donors.
- Facilitate comprehensive brain death certification and organ donation counselling.
- Strengthen the organ transplantation infrastructure nationwide.
Guidelines are to be evolved to safeguard live donors from exploitation and ensure their post-donation care.
Water Budgeting for Aspiration Blocks
Why in news?
Water Budgeting in Aspirational Blocks is a significant initiative by NITI Aayog aimed at enhancing local water security through effective water management at the block level.
Methodology and Tools
- Utilizes a web-based platform called Varuni for water budgeting.
- Estimates water demand across key sectors: human, livestock, agriculture, and industry.
- Accounts for supply from multiple water sources like runoff, surface water, groundwater, and water transfers.
- Provides a scientific, user-friendly methodology for preparing water budgets at the block level.
- Blocks were selected based on water stress levels, groundwater data, and tap water coverage under Jal Jeevan Mission.
Key Findings and Insights
- Identifies water demand-supply gaps and hotspots of water consumption, especially in irrigation and livestock sectors.
- Highlights the importance of customized, localized water management strategies specific to each block’s water endowment.
- Reveals how industrial water use, though localized, can create stress points.
- Emphasizes convergence in national water programs for integrated, anticipatory planning rather than reactive management.
Objectives and Outcomes
- To enable informed decision-making for sustainable water management and efficient utilization at the local level.
- To promote equitable distribution and resilience in water availability.
- To involve communities in improving water access with measurable impact on livelihoods and health.
- To assist in transitioning towards climate resilience and sustainable development through data-driven governance.
Policy Implications
- Facilitates proactive water management using digital governance tools.
- Encourages coordination of various government schemes like MGNREGA, Jal Jeevan Mission, watershed programs for enhanced water security.
- Serves as a diagnostic and planning tool for future water resource challenges at the grassroots level.
Kodaikanal Solar Observatory (KoSO)
About
- The Kodaikanal Solar Observatory (KoSO), established in 1899 and owned by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics, is one of India's most significant scientific institutions for solar studies.
- Located near Kodaikanal in Tamil Nadu, its mission originated from the need to understand the link between solar activity and the Indian monsoon, especially after a severe famine in the 1890s.
- The Evershed effect (radial flow of gas in sunspots) was first discovered here in 1909.
- Pioneered systematic, daily solar observations (notably in Ca II K wavelength since 1904), capturing chromospheric activity and solar magnetism over a century.
- Equipped with high-powered telescopes, solar tower, spectroheliographs, a solar tunnel telescope, and archival photographic plates.
Current Research and Applications
- Researchers have reconstructed the Sun's polar magnetic field spanning the last 100 years using KoSO's archive, greatly improving accuracy in predicting solar storms and understanding space weather.
- KoSO's digitized historical data is now a critical global resource for AI and machine learning studies in solar physics.
- KoSO regularly conducts ionospheric and geomagnetic observations. Data is shared with the India Meteorological Department and World Meteorological Organization for global weather and climate studies.
Goldilocks Environment
Why in news?
Morgan Stanley's 2026 India Economics Outlook projects that India's economy is currently experiencing a "Goldilocks environment," and this phase will continue with domestic demand as the key driver amid uncertain external conditions.
About Goldilocks Environment
- A Goldilocks Environment, often referred to as a Goldilocks economy, is an ideal economic condition characterized by balanced and moderate economic growth, low inflation, and near-full employment.
- It is an economic state that is "just right" — not growing too fast to cause overheating and high inflation, nor too slow to risk recession or stagnation.
- This balance creates a stable environment favorable for investment and sustainable growth.
- Market-friendly monetary policy due to balanced economic indicators.
- It tends to be a transitional phase within the business cycle, commonly during recovery or growth phases.
Importance and Implications
- The Goldilocks state facilitates investor confidence as companies grow earnings steadily.
- Central banks use monetary policies such as interest rate adjustments to maintain this balance.
- It is often temporary, as economic activities naturally cycle through expansions and contractions.
- This environment supports stable consumer spending, moderate business investment, and manageable inflation pressures.
The phrase "Goldilocks environment" is also used beyond the economy to refer to any situation balanced between extremes, such as the "Goldilocks zone" in astronomy, indicating the habitable zone around a star where conditions are "just right" for liquid water and potentially life.
Why in news?
The CE20 Cryogenic Engine, developed by ISRO, has recently demonstrated successful operation under vacuum conditions—specifically, a "boot-strap mode" start test without any auxiliary start-up system.
About CE20 engine
- Indigenous LOX–LH2 cryogenic engine developed by ISRO’s Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre.
- Powers the C25 cryogenic upper stage of LVM3 (GSLV Mk?III).
Significance of vacuum testing
- Simulates the nearzero atmospheric pressure of space, ensuring CE20 can ignite and run exactly as it will on the LVM3 upper stage in orbit.
- Confirms that propellant flow, combustion stability, and nozzle expansion behave correctly when there is no surrounding air.
- Carried out at the High?Altitude Test (HAT) facility, Mahendragiri (Tamil Nadu), which uses pumps and chambers to create space like vacuum and realistic tank pressures.
- Successful ignition and steady operation under these conditions proves the engine is flight ready for critical missions like Gaganyaan human spaceflight.
Bootstrap mode start: A Major Innovation
- Conventional cryogenic engines in space use an auxiliary start system (e.g., stored highpressure gas) to spin turbopumps, adding mass and complexity.
- In bootstrap mode, CE20 spins up its turbopumps and builds pressure using its own gas?generator and propellant flow, without any external startgas system.
- A multielement igniter in both the thrust chamber and gas generator enables this autonomous start and smooth transition to steadystate operation in vacuum.
- This method increases payload capacity, simplifies stage hardware, and is regarded as a worldfirst demonstration for a gasgeneratorcycle cryogenic engine, enhancing flexibility and efficiency of future LVM3 missions.
Download Pdf