CA-20/11/2025
New Genome editing technology based on TnpB
Why in news?
- Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) has developed and patented a new indigenous gene editing technology based on TnpB (transposon-associated proteins) as a "miniature alternative" to CRISPR-Cas.
- This allows precise, cheaper genome editing in crops, reducing dependency on patented CRISPR-Cas technology.
About TnpB (transposon-associated proteins)
- It is a tiny protein that helps transposons (bits of DNA that can move around in the genome) to cut and insert DNA at specific places.
- It is found in certain mobile genetic elements called transposons.
- TnpB uses a small RNA guide (called ωRNA) to find and cut specific DNA sequences, similar to how CRISPR systems work, but TnpB is much smaller.
- TnpB called a "miniature" tool because it is much smaller in size(~400 amino acids) compared to other gene-editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9(~1000–1400 aa), making it easier to deliver into cells and use in therapies or experiments.
- TnpB can be programmed to cut DNA at specific sites, which could make it useful for editing genes in humans, plants, or animals, similar to CRISPR but with simpler delivery and possibly fewer side effects.
- TnpB has the potential to be a cheaper, easier, and smaller alternative to current gene-editing tools, opening new possibilities for medicine and agriculture.
Comparison with CRISPR-Cas9/Cas12
- Advantages vs Cas9/Cas12: far smaller size, easier viral delivery, potential to target genomic regions not accessible to standard PAM-dependent systems, and fully indigenous toolchains in some countries (e.g., India).
- Limitations: editing efficiencies and TAM compatibility are still being optimized, off-target and collateral activities need systematic characterization, and the tool is less mature than widely used Cas9/Cas12 platforms.
Ratanmahal Wildlife Sanctuary
Why in news
- A young male tiger has settled permanently in the sanctuary for nine months, marking Gujarat's longest tiger presence in modern history.
- Gujarat now becomes one of the few Indian states hosting lions, leopards, and tigers together within its natural landscape, emphasizing ecological success.
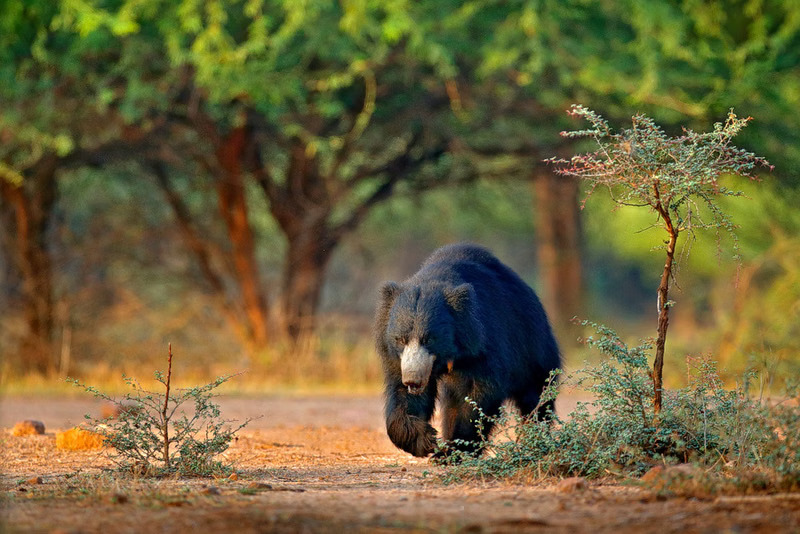
About Ratanmahal Wildlife Sanctuary
- Location and Size: It is situated in Dahod district of Gujarat, covering approximately 55 to 80 square kilometers, at the Gujarat-Madhya Pradesh border, with rugged, hilly terrain and mixed deciduous forests.
- Flora: The sanctuary features dry teak forests, mixed deciduous forests, dry bamboo brakes, and patches of timru and sadad trees, alongside Mahuda and Jamun trees, which serve as primary food sources for wildlife, especially sloth bears.
- Fauna: It is home to a significant sloth bear population, along with leopards, striped hyenas, four-horned antelopes, jungle cats, hyenas, and recently, sightings of tigers, making it a rich biodiversity hotspot.
- Ecological Significance: The sanctuary forms the catchment area for the Panam River, playing a crucial role in water conservation and regional ecology.
- Dahod Ratanmahal wildlife Sanctuary, established in 1982, is renowned for harboring the largest population of sloth bears in Gujarat
Public Distribution System (PDS)
Why in news?
The government has launched several new initiatives in 2025 to improve the Public Distribution System (PDS), focusing on digital transformation, supply chain efficiency, transparency, and enhanced service delivery to beneficiaries.
Key New Initiatives
- Digital Warehousing Modernization: Initiatives such as Bhandara 360, Smart EXIM Warehouse, Anna Darpan cloud-based platforms, and a modern SILO facility at Malout, Gujarat, have been launched to modernize warehousing operations, reduce logistics costs, and minimize turnaround time in food distribution. These aim to strengthen the supply chain efficiency and provide accurate and dignified delivery of food grains.
- Anna Sahayata Holistic AI Solution (ASHA): A cutting-edge AI-powered solution implemented with backing from the India AI Mission and the Wadhwani Foundation. ASHA enables beneficiaries to report on the receipt of full entitlements, quality of food grains, and issues faced at Fair Price Shops. It integrates with 35 external systems for seamless data flow and transparency.
- Real-time Digital Monitoring and Security Enhancements: Introduction of single sign-on, role-based access, end-to-end data encryption, real-time dashboards, automated workflows including chatbots and robotic process automation (RPA), and predictive analytics to support faster decision-making and better monitoring from warehouses to corporate levels.
- One Nation-One Ration Card (ONORC) Scheme: Continuation and expansion of the ONORC scheme enable nationwide portability of ration cards, allowing beneficiaries to access PDS from anywhere in India. Monitoring and awareness efforts include SMS notifications for stock status, transactions, and scheme updates in local languages.
- Grievance Redressal and Beneficiary Cleanup: Use of Aadhaar-seeding and data analytics has led to removing ineligible beneficiaries to curb leakage and improve targeting. The government is also focusing on strengthening grievance redressal at various administrative levels, ensuring timely and accessible redress for beneficiaries.
- SMART-PDS Scheme: Approved for 2023-2026, SMART-PDS updates technology and management systems from previous computerization schemes, aiming at continuous modernization and improvement in PDS operations.
Significance and Expected Impact
- These initiatives are expected to significantly improve the efficiency, transparency, and responsiveness of the PDS.
- Reduction in logistics costs and minimization of turnaround time.
- Better coordination between stakeholders to ensure timely and accurate delivery of subsidized food grains.
- Enhanced beneficiary participation and feedback through AI and digital tools.
- Overall strengthening of India's food security framework for over 78 crore beneficiaries under the National Food Security Act.
Tetrachloroethylene
Why in news?
- Tetrachloroethylene (also called perchloroethylene or PCE), a chemical widely used in dry cleaning and household products, has been linked to a tripling of the risk of significant liver diseases, including liver fibrosis, liver cancer, and liver failure.
- PCE exposure occurs through air, water contamination, and products like adhesives and spot cleaners.
About
- Tetrachloroethylene, also known as perchloroethylene or perc (chemical formula C2Cl4),
- a non-flammable, stable, colorless, and dense liquid.
- Reacts with water to form dichloromethane and oxygen
- Insoluble or slightly soluble in water
- Nonflammable and chemically stable under normal conditions
- Exposure can cause dizziness, headaches, nausea, and irritation of eyes, skin, and respiratory tract
Uses and Applications
- Widely used as a solvent in dry cleaning of fabrics
- Employed as a metal degreasing solvent in industry
- Used in adhesives, paint removers, inks, and electrical transformer cooling fluids
Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS)
Why in news?
- The European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) has created a new scoring system to measure how active and serious antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is in a person.
- It looks at different symptoms and lab test results to give a clear number that shows whether the disease is mild, moderate, or severe at a given time.
- Doctors can use this number to understand how the disease is changing, whether treatments are working, and what kind of care a patient might need.
About antiphospholipid syndrome (APS)
- APS involves the immune system mistakenly producing antibodies that attack tissues in the body, leading to abnormal blood clot formation in arteries and veins and various organs.
- It also affects pregnancy, leading to miscarriages, stillbirths, and other pregnancy morbidities.
- The causes involves autoimmune mechanisms where antiphospholipid antibodies attack phospholipid-binding proteins.
- There is currently no cure, but treatments focus on reducing clotting risk and pregnancy loss.
- Current treatments for Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) mainly include medicines called anticoagulants or blood thinners, such as heparin and warfarin.
- In addition, some patients are given antimalarial drugs like hydroxychloroquine, which can help protect blood vessels and prevent problems with pregnancy related to APS.
Trade Intelligence and Analytics (TIA) Portal
Why in news?
- The TIA Portal is a newly launched, comprehensive digital platform by the Department of Commerce, Government of India, designed to provide accessible, real-time trade data and analytics to exporters, importers, MSMEs, startups, policymakers, and other stakeholders.
- The portal offers a user-centric, cost-effective, open-source solution integrating multiple national and global trade databases including bilateral trade data and macroeconomic indicators.
Key features of the TIA Portal
- Unified System: It brings together multiple trade databases, including international sources like UN Comtrade, and national data, into one platform.
- Extensive Data Access: Offers over 270 visualizations and 28 dashboards for detailed trade analysis, covering India’s trade with more than 220 countries.
- Real-time Insights: Provides live, interactive data on global and Indian trade trends, sector performance, commodities, and export opportunities.
- User-Friendly: Designed to be accessible, scalable, and affordable, with no licensing costs and minimal infrastructure needs.
- Advanced Analytics: Includes tools to compare trade indicators, identify market opportunities, and assess competitiveness using indices like Trade Complementarity and Revealed Comparative Advantage.
- Automated Reports: Generates periodic trade reports and alerts, helping stakeholders stay updated on trade trends and sector performance.
The portal aims to enable transparent, data-driven decisions to strengthen India’s global trade presence, optimize strategies amid global tariff volatility, and expand export opportunities across sectors including manufacturing under production-linked incentive (PLI) schemes and critical minerals trade.
Viscose Staple Fibre (VSF)
Why in news?
- The Indian government has revoked the Quality Control Order (QCO) for VSF, aiming to address raw material accessibility and promote industry growth, making the fiber more accessible and reducing regulatory hurdles.
About VSF
- A natural, biodegradable, and man-made fiber derived primarily from cellulose sources such as wood pulp and cotton linters.
- Chemically resembles cotton but is man-made and can be engineered for different properties.
- Provides excellent color retention, lightweight feel, and high moisture absorbency.
- Versatile in texture and can be blended with natural and synthetic fibers.
Applications:
- Extensively used in fashion and apparel industries.
- Used for home textiles, dress materials, knitted wear, and non-woven products.
- Blending with other fibers enhances textile quality and versatility.
Environmental Aspects
- Despite its benefits, the production of VSF is energy-intensive and involves processes that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
- The fiber is produced from wood pulp sourced primarily through deforestation, which poses ecological concerns.
SC invalidate Tribunal reform provision
Why in news?
- The Supreme Court of India has struck down key provisions of the Tribunals Reforms Act, 2021, declaring them unconstitutional.
- The Court ruled that these provisions violated the principles of judicial independence and separation of powers.
Key points for invalidation
- Government control over tenure and age limits for tribunal members.
- Inclusion of government secretaries in selection committees.
- Limiting tribunal member tenure to four years, affecting institutional stability.
- Excessive rule-making powers to the executive over tribunals.
| Principle |
Key Aspects |
Purpose/Significance |
| Judicial Independence |
Fair, impartial adjudication; no external influence; exclusive judicial jurisdiction; security of tenure |
Ensures rule of law, fair trials, protects rights |
| Separation of Powers |
Division of state powers into legislature, executive, judiciary; mutual checks and balances |
Prevents power concentration, safeguards liberty |
National cooperative development corporation (NCDC)
Why in news?
- In recent years, NCDC has expanded its scope to include financing projects in rural industrial cooperative sectors and notified services such as water conservation, irrigation, micro-irrigation, agri-insurance, rural sanitation, and animal health.
- The corporation has also been instrumental in promoting the circular economy in sectors like sugar mills and dairy, directly benefiting farmers and rural communities.
About NCDC
- Statutory organization under the Ministry of Cooperation, Government of India.
- Established in 1963 by an Act of Parliament.
- Headquarters in New Delhi with multiple regional and state offices.
- Supports cooperative development in agriculture and rural sectors.
Functions of NCDC
- Provides financial assistance to cooperatives for agriculture, food processing, marketing, storage, and allied activities.
- Finances projects in dairy, poultry, fisheries, handloom, sericulture, and rural industries.
- Extends loans and grants to primary, secondary, and national cooperative societies.
- Promotes and supports farmer producer organizations (FPOs) and PACS.
- Implements schemes for rural infrastructure, animal health, irrigation, and sanitation.
Objectives of NCDC
- Foster self-reliant, sustainable cooperative societies.
- Promote inclusive rural development and livelihood enhancement.
- Support weaker sections including scheduled castes, tribes, and women cooperatives.
- Accelerate cooperative-led economic growth and employment generation in rural areas.
Schemes and Initiatives to strengthen cooperatives
- Yuvika Scheme: Focuses on promoting youth entrepreneurship in the cooperative sector.
- Integrated Cooperative Development Project (ICDP): Aims at holistic development of districts through cooperative activities.
- Relief in Income Tax Law: Provides tax benefits to cooperative societies.
- Strengthening of Rural Cooperative Banks: Enhances financial inclusion and access to credit for rural populations.
- Support for PACS (Primary Agricultural Credit Societies): Facilitates their transformation into Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs) for better market access and fair prices for farmers.
Significance and Impact
- Serving over 13,000 cooperative societies with approximately 2.9 crore members.
- Enabling inclusive rural growth through job creation, especially in women-led and labor cooperatives.
- Supporting cooperatives in cold storage, food processing, fisheries, dairy, and textiles, thereby enhancing value chains and rural livelihoods.
- Achieving a compound annual growth rate of over 40%, maintaining zero net non-performing assets (NPA), and registering its highest-ever net profit of 807 crore in recent years.
Ultra-processed foods (UPFs)
Why in news?
Ultra-processed foods (UPFs) growing global public health concern due to their strong association with chronic diseases including obesity, diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, cancer, mental health disorders and higher mortality rates.
About Ultra-processed foods
- Ultra-processed foods (UPFs) are industrial formulations made mostly from substances extracted or refined from whole foods, often with many additives.
- They contain ingredients like sugar, fat, salt, preservatives, colorings, flavor enhancers, emulsifiers, and other additives not usually found in home cooking.
- They reduce satiety and encourage overeating through their hyper-palatable taste and high energy density.
- UPFs tend to be high in calories, sugar, unhealthy fats, and salt while being low in fiber, protein, vitamins, and minerals.
- Examples include packaged snacks, soft drinks, ready meals, processed meats, sweetened drinks, cakes, ice cream, burgers, and instant noodles.
- They are designed for profitability, convenience, long shelf life, and aggressive marketing, often targeting youth and middle-income consumers.
Why in news?
Killing of Madvi Hidma, a top Maoist commander is expected to trigger a further wave of Maoist surrenders and indicate a weakening of Maoist military leadership.
Historical backgouund
- Originated from the 1967 Naxalbari uprising in West Bengal, beginning as a peasant movement inspired by Maoist ideology.
- The movement led to the formation of various Maoist groups fighting an armed rebellion against the Indian state.
- Spread across eastern, central, and southern India, covering many districts in states like Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha, Bihar, Maharashtra, and Andhra Pradesh.
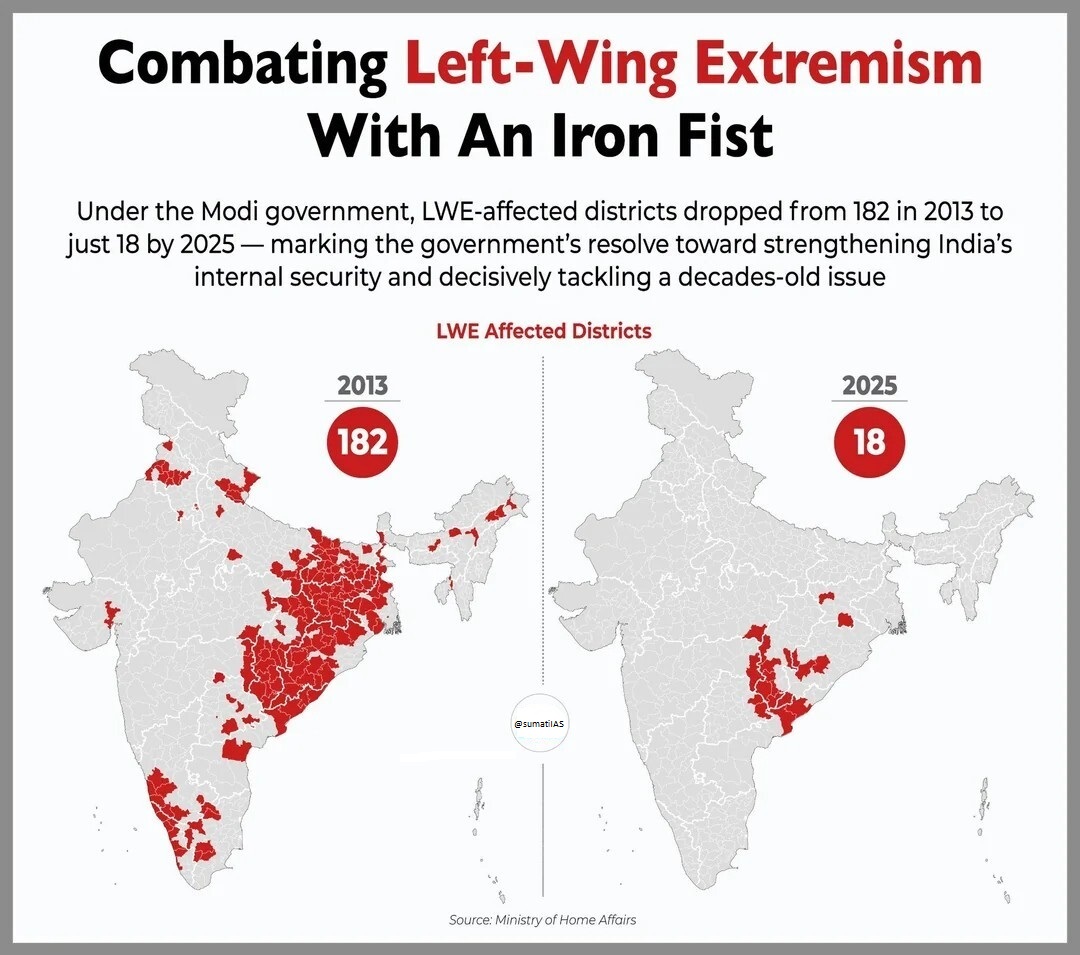
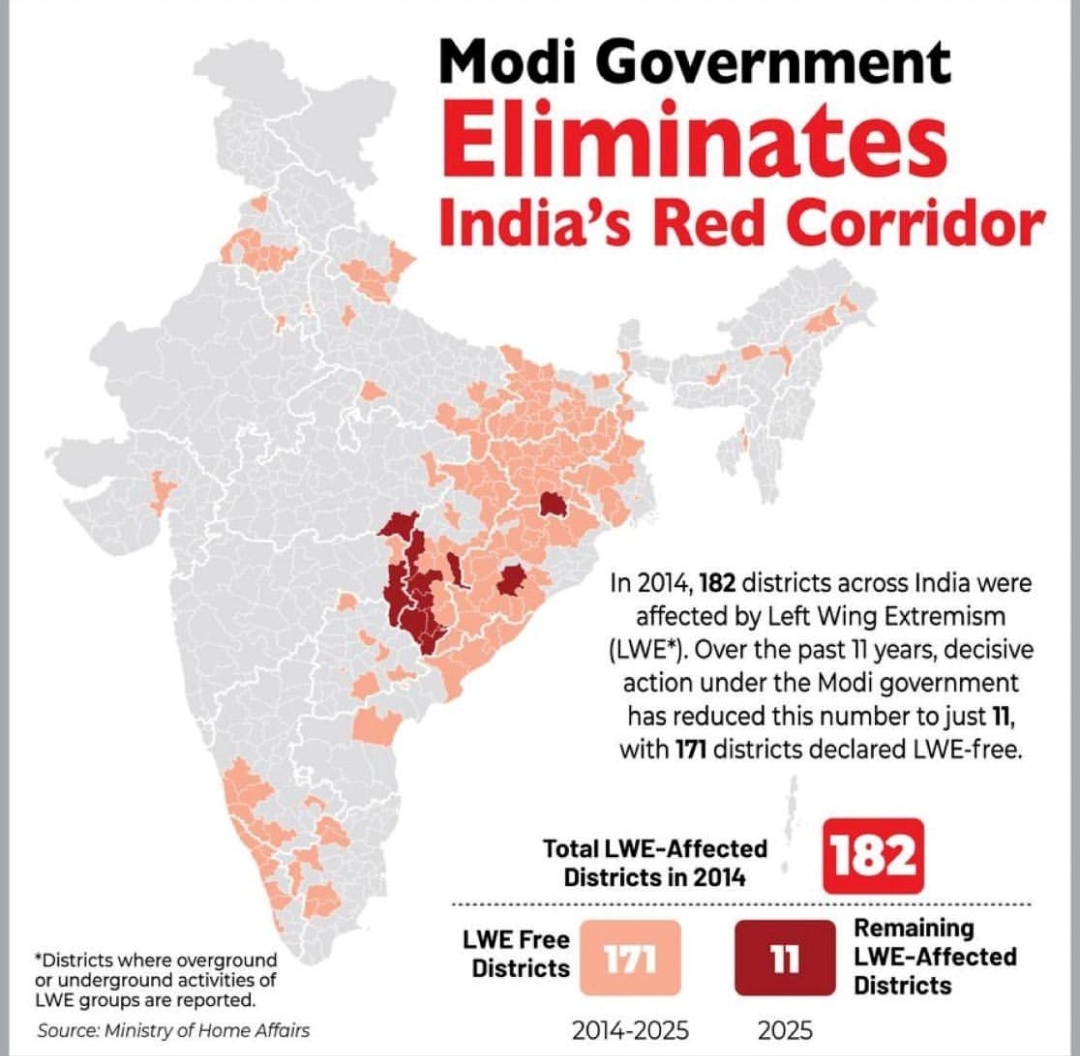
- At its peak in the late 2000s, the Red Corridor affected nearly 180 districts known for Naxalite-Maoist insurgency.
- The insurgency involved guerrilla warfare, extortion, attacks on security forces, destruction of infrastructure, and parallel governance.
- Naxalites gained influence in impoverished, underdeveloped regions where government presence was weak, sometimes acting as alternate authority.
Present Situation (2025):
- It has significantly shrunk due to government counter-insurgency operations and developmental efforts.
- As of March 2025, only about 18 districts across 7 states remain affected, down from 182 districts in 2013.
- The corridor is largely limited to parts of Central and Eastern India, with 6 districts classified as 'most affected'.
- Security forces have regained control over previously inaccessible areas; development activities have increased including roads, schools, hospitals, and banking.
- The government aims to eradicate Naxalism by 2026.
- The Red Corridor is transitioning from a conflict zone to growth corridors marked by infrastructure and social development.
- The Maoist insurgency’s strategic and operational capability has diminished considerably.
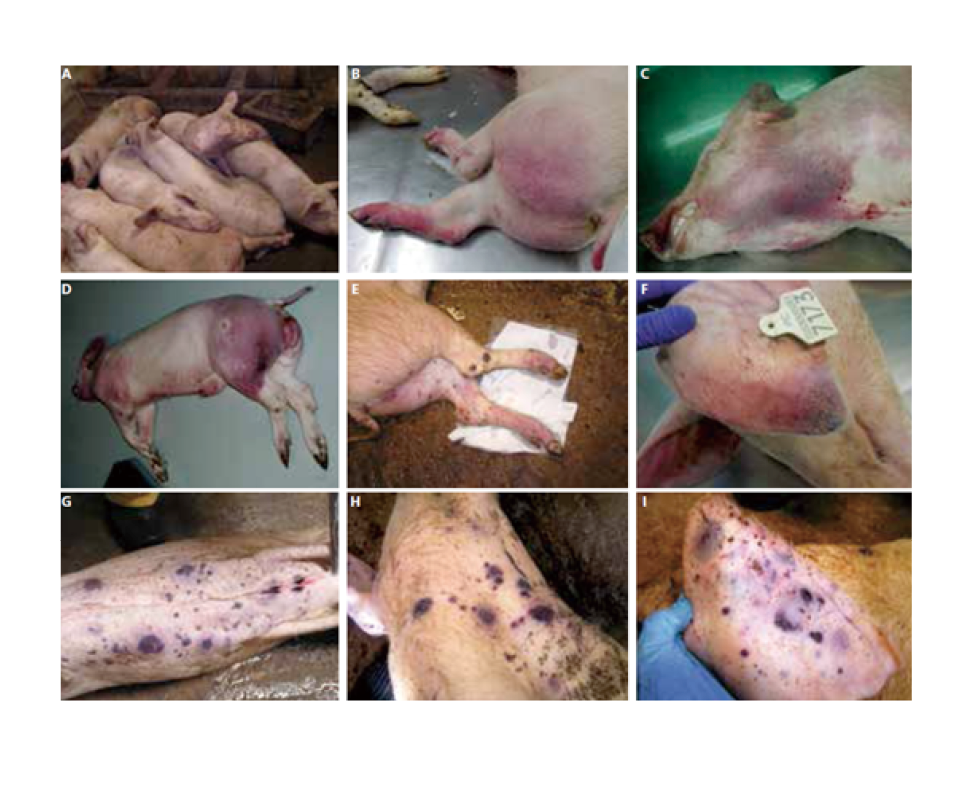
African swine fever (ASF)
- ASF is a viral hemorrhagic fever of pigs, fatal in many cases.
- Caused by African swine fever virus (ASFV), a large, double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the Asfarviridae family.
- Endemic in sub-Saharan Africa, transmitted by wild pigs and ticks.
- Does not affect humans.
- Symptoms: high fever, hemorrhages, cyanosis, respiratory distress, abortions, death.
- Mortality up to 100% in acute forms.
- No commercial vaccine yet; control by biosecurity and culling.
Economic Impact
- Direct losses to farmers come from pig mortality and culling.
- Indirect losses affect the entire supply chain, including feed suppliers, veterinary services, meat processors, and traders.
- Outbreaks lead to significant declines in household and rural farm incomes.
- Trade restrictions on pork from ASF-affected countries further disrupt markets internationally.
Leadership Group for Industry Transition (LeadIT)
Why in news?
Union Environment Minister highlighted progress made under the Industry Transition Platform (ITP), funded by India and Sweden, with 18 industries and research institutions from both countries beginning projects on carbon capture, AI for process optimization, electrification, and hydrogen heating.
About Industry Transition Platform (ITP)
- The Industry Transition Platform (ITP) is an initiative under the Leadership Group for Industry Transition (LeadIT) launched by the Prime Ministers of India and Sweden at COP28 in 2023.
- It aims to accelerate the decarbonization of heavy industries, specifically focusing on the steel and cement sectors.
Key features of LeadIT
- It was launched by the governments of Sweden and India at the UN Climate Action Summit in 2019.
- Focus on inclusive and just industry transitions, low-carbon technology development and achieving net-zero carbon emissions in energy-intensive industries by 2050.
- Supported by the World Economic Forum, LeadIT facilitates public-private collaboration, sectoral and cross-sectoral learning, and technology transfer.
- A platform for political, industrial, financial, and climate leaders to share expertise and advance policies for industry decarbonization.
- Hosting roadmaps, dialogues, and partnerships to support industry transition.
- Around 37 members including countries like India, Sweden, Japan, South Africa, and companies committed to climate goals.
- Secretariat hosted by the Stockholm Environment Institute and managed by a board with members from Sweden, India, and the World Economic Forum.
- LeadIT has also launched LeadIT 2.0 to further its mission through enhanced global dialogue, technology collaboration, and fostering partnerships for inclusive transition.
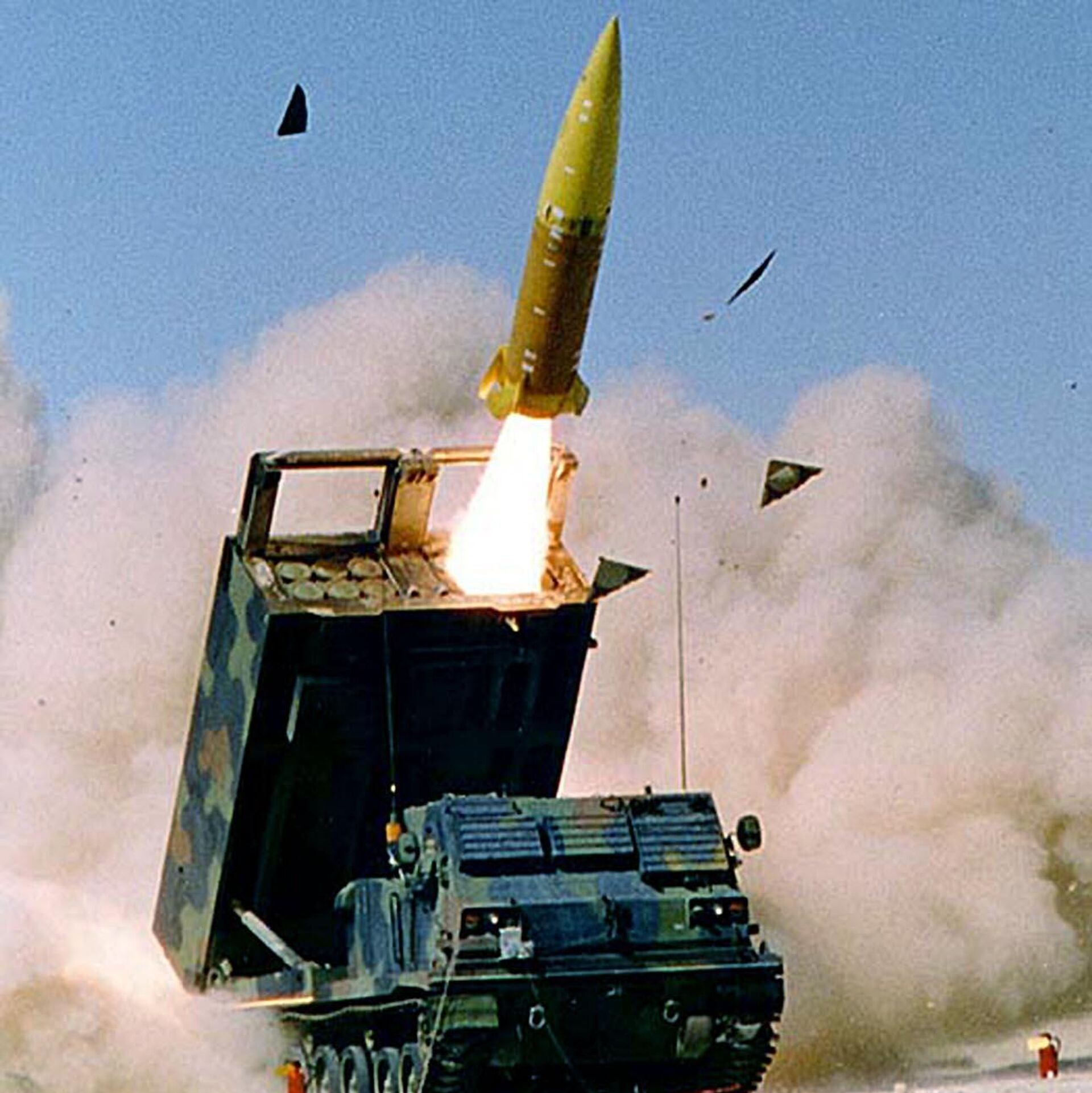
Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS)
Why in news?
In November 2025 highlights that Ukraine has launched U.S.-supplied Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) missiles against military targets inside Russia.
Features of ATACMS
- Made by Lockheed Martin, Surface-to-surface ballistic missile system launched from HIMARS and M270 MLRS platforms.
- Precision-guided using inertial navigation and GPS ensuring high accuracy for both stationary and moving targets.
- Operational range up to approximately 300 km depending on the variant.
- Payload options include unitary high-explosive warheads and cluster munitions.
- Travels at speeds over Mach 3, making it difficult to intercept.
- Compatible with multiple launch platforms for battlefield flexibility.
- The U.S. Army has announced plans to replace ATACMS with the Long Range Precision Fires (LRPF) missile system, which will offer even greater range and precision.
Its ability to strike deep into enemy territory allows ground forces to disrupt enemy operations and degrade their capabilities before direct engagement.
Questions and Answers
Question 1. Consider the following statements about African Swine Fever (ASF):
1. It is a viral hemorrhagic fever that primarily affects pigs and can be fatal.
2. It is caused by a large, double-stranded DNA virus.
3. A commercially available vaccine is widely used for prevention.
4. It is known to affect humans, causing severe respiratory illness.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1, 3 and 4 only
C) 2 and 4 only
D) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: ASF is a viral hemorrhagic fever of pigs, fatal in many cases. Statement 2 is correct: It is caused by African swine fever virus (ASFV), a large, double-stranded DNA virus. Statement 3 is incorrect: The text explicitly states, 'No commercial vaccine yet.' Statement 4 is incorrect: The text clearly states, 'Does not affect humans.'
Question 2. With reference to Viscose Staple Fibre (VSF), consider the following statements:
1. It is a natural, biodegradable, and man-made fiber derived primarily from cellulose sources.
2. Its production is energy-intensive and contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
3. The Indian government has recently issued a Quality Control Order (QCO) for VSF to ensure its quality for export.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 only
B) 1 and 2 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2 and 3
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: VSF is derived from cellulose sources and is a natural, biodegradable, and man-made fiber. Statement 2 is correct: Its production is energy-intensive and contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, with ecological concerns regarding deforestation. Statement 3 is incorrect: The Indian government has revoked the Quality Control Order (QCO) for VSF, aiming to address raw material accessibility and promote industry growth, not issued it.
Question 3. Consider the following statements regarding the 'Trade Intelligence and Analytics (TIA) Portal':
1. It is a digital platform launched by the Ministry of Finance to monitor foreign exchange reserves.
2. It integrates multiple national and global trade databases for real-time insights.
3. It is designed to be user-centric, cost-effective, and open-source, with no licensing costs.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 3 only
D) 1, 2 and 3
Explanation:
Statement 1 is incorrect: The TIA Portal is a comprehensive digital platform launched by the Department of Commerce, Government of India, to provide trade data and analytics, not by the Ministry of Finance for foreign exchange reserves. Statements 2 and 3 are correct as per the provided information, highlighting its data integration capabilities, user-centric design, cost-effectiveness, and open-source nature.
Question 4
Regarding the 'Red Corridor' in India, which of the following statements is correct as per the provided information?
A) The Red Corridor originated from the peasant movement in Telangana in the 1940s.
B) At its peak, the Red Corridor affected approximately 18 districts across various states.
C) As of March 2025, the number of affected districts has significantly shrunk to about 18, largely in Central and Eastern India.
D) The government aims to eradicate Naxalism by 2030, transitioning these areas into industrial hubs.
Explanation:
Statement (a) is incorrect; it originated from the 1967 Naxalbari uprising in West Bengal. Statement (b) is incorrect; at its peak, it affected nearly 180 districts. Statement (c) is correct; as of March 2025, only about 18 districts across 7 states remain affected. Statement (d) is incorrect; the government aims to eradicate Naxalism by 2026, not 2030.
Question 5. What is a key feature of the Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS)?
A) It is an air-to-air missile primarily used for intercepting enemy aircraft.
B) It is a surface-to-surface ballistic missile system with an operational range up to approximately 300 km.
C) It is a defensive anti-tank missile designed for close-range combat.
D) It is a naval cruise missile used for long-range maritime strikes.
Explanation:
The provided text describes ATACMS as a 'Surface-to-surface ballistic missile system' with an 'Operational range up to approximately 300 km'. The other options describe different types of missile systems not aligning with the description of ATACMS.
Question 6. With reference to the recent initiatives to improve the Public Distribution System (PDS) in India, consider the following statements:
1. The 'Anna Sahayata Holistic AI Solution (ASHA)' is designed to enable beneficiaries to report issues at Fair Price Shops and provides real-time data flow.
2. The 'One Nation-One Ration Card (ONORC)' scheme has been discontinued due to implementation challenges.
3. 'SMART-PDS Scheme' is approved for 2023-2026 for continuous modernization of PDS operations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 only
B) 1 and 3 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2 and 3
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: ASHA is an AI-powered solution enabling beneficiaries to report on entitlements, quality, and issues. Statement 2 is incorrect: The ONORC scheme is stated to be under 'continuation and expansion,' not discontinued. Statement 3 is correct: SMART-PDS Scheme is approved for 2023-2026 for continuous modernization. Thus, 1 and 3 are correct.
Question 7. Consider the following statements about Ratanmahal Wildlife Sanctuary:
1. It is situated in the Dahod district of Gujarat.
2. It is renowned for harboring the largest population of lions in Gujarat.
3. The sanctuary forms the catchment area for the Panam River.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 1, 2 and 3
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: Ratanmahal Wildlife Sanctuary is situated in the Dahod district of Gujarat. Statement 2 is incorrect: It is renowned for harboring the largest population of sloth bears in Gujarat, not lions. Statement 3 is correct: The sanctuary forms the catchment area for the Panam River. Therefore, 1 and 3 are correct.
Question 8. Tetrachloroethylene, often linked to significant liver diseases, is widely used in which of the following applications?
1. Dry cleaning of fabrics
2. Metal degreasing solvent in industry
3. As a primary component in cooking oils
4. For enhancing the nutritional value of processed foods
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 1, 3 and 4 only
C) 2 and 4 only
D) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Explanation:
Tetrachloroethylene (PCE) is widely used as a solvent in dry cleaning of fabrics and as a metal degreasing solvent in industry. It is also used in adhesives, paint removers, inks, and electrical transformer cooling fluids. It is not used in cooking oils or for enhancing nutritional value of processed foods. Hence, statements 1 and 2 are correct.
Question 9. Which of the following characteristics are typically associated with Ultra-processed foods (UPFs)?
1. They are industrial formulations often made from substances extracted or refined from whole foods.
2. They are generally high in fiber, protein, vitamins, and minerals.
3. They are designed for profitability, convenience, and long shelf life.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A) 1 only
B) 1 and 2 only
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 1, 2 and 3
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: UPFs are industrial formulations made mostly from substances extracted or refined from whole foods, often with many additives. Statement 2 is incorrect: UPFs tend to be low in fiber, protein, vitamins, and minerals, while being high in calories, sugar, unhealthy fats, and salt. Statement 3 is correct: They are designed for profitability, convenience, long shelf life, and aggressive marketing. Therefore, 1 and 3 are correct.
Question 10. With reference to the Leadership Group for Industry Transition (LeadIT), consider the following statements:
1. It was launched by the governments of Sweden and India at the UN Climate Action Summit in 2019.
2. Its primary focus is to accelerate the decarbonization of heavy industries like steel and cement.
3. The secretariat for LeadIT is hosted by the World Economic Forum.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 only
B) 1 and 2 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2 and 3
Explanation:
Statement 1 is correct: LeadIT was launched by the governments of Sweden and India at the UN Climate Action Summit in 2019. Statement 2 is correct: Its focus is on achieving net-zero carbon emissions in energy-intensive industries by 2050, specifically mentioning steel and cement sectors through the Industry Transition Platform (ITP). Statement 3 is incorrect: The secretariat for LeadIT is hosted by the Stockholm Environment Institute, although it is supported by the World Economic Forum.
Question 11. Which of the following best describes Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS)?
A) It is a genetic disorder primarily affecting bone density.
B) It is an autoimmune condition leading to abnormal blood clot formation and affecting pregnancy.
C) It is a bacterial infection causing severe respiratory distress.
D) It is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by progressive memory loss.
Explanation:
Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) involves the immune system mistakenly producing antibodies that attack tissues in the body, leading to abnormal blood clot formation in arteries and veins and various organs. It also affects pregnancy, leading to miscarriages, stillbirths, and other pregnancy morbidities.
Question 12. Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the newly developed indigenous gene editing technology based on TnpB?
1. It is a miniature alternative to CRISPR-Cas, making it easier to deliver into cells.
2. It uses a small RNA guide (ωRNA) to find and cut specific DNA sequences.
3. It has limitations such as being less mature than Cas9/Cas12 platforms and still optimizing editing efficiencies.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 1 and 2 only
D) 1, 2 and 3
Explanation:
All three statements are correct. TnpB is indeed a miniature alternative to CRISPR-Cas, making delivery easier. It uses a small RNA guide (ωRNA) similar to CRISPR. The text also mentions its limitations including being less mature and still optimizing efficiencies compared to Cas9/Cas12 platforms.
Question 13. The Supreme Court of India recently invalidated key provisions of the Tribunals Reforms Act, 2021. This decision was primarily based on the violation of which of the following constitutional principles?
A) Federalism and decentralization of power
B) Judicial independence and separation of powers
C) Right to equality and non-discrimination
D) Parliamentary sovereignty and legislative supremacy
Explanation:
The Supreme Court ruled that the provisions of the Tribunals Reforms Act, 2021, violated the principles of judicial independence and separation of powers. Key points for invalidation included government control over tenure and age limits for tribunal members, inclusion of government secretaries in selection committees, and limiting tribunal member tenure, all impinging on judicial autonomy.
Question 14. Which of the following statements about the National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC) is/are correct?
1. It is a statutory organization under the Ministry of Cooperation.
2. It provides financial assistance to cooperatives for agriculture, food processing, and allied activities.
3. The 'Yuvika Scheme' is one of its initiatives focusing on youth entrepreneurship in the cooperative sector.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Select your answer:
A) 1 only
B) 1 and 2 only
C) 2 and 3 only
D) 1, 2 and 3
Explanation:
All three statements are correct. NCDC is a statutory organization under the Ministry of Cooperation, established in 1963. It provides financial assistance to cooperatives across various sectors including agriculture and food processing. The Yuvika Scheme is explicitly mentioned as one of its initiatives focusing on youth entrepreneurship in the cooperative sector.
Question 15. Which of the following initiatives are aimed at strengthening cooperative societies or improving the Public Distribution System (PDS) in India?
1. Yuvika Scheme
2. Anna Sahayata Holistic AI Solution (ASHA)
3. One Nation-One Ration Card (ONORC) Scheme
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 1, 2 and 3
Explanation:
The 'Yuvika Scheme' is mentioned as an NCDC initiative focusing on youth entrepreneurship in the cooperative sector, thus strengthening cooperative societies. 'Anna Sahayata Holistic AI Solution (ASHA)' and 'One Nation-One Ration Card (ONORC) Scheme' are both listed as key new initiatives to improve the Public Distribution System (PDS). Therefore, all three initiatives align with the question's premise.
Download Pdf