CA-14/11/2025
News reports have confirmed that the DNA of the suspected bomber, Dr. Umar Nabi Bhat, matched the human remains found at the blast site.
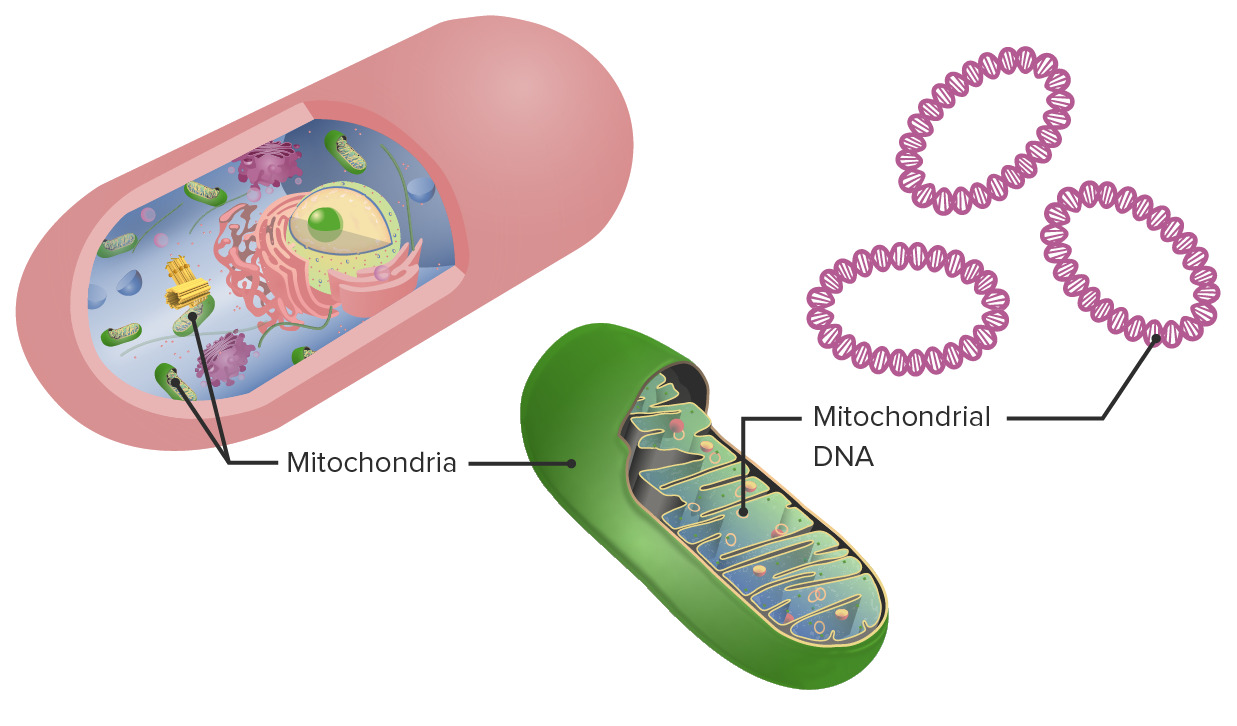
DNA tests, which would include mitochondrial DNA analysis if standard nuclear DNA was unviable due to the condition of the remains, have confirmed that Dr. Umar Nabi Bhat was the individual in the car that exploded near the Red Fort in Delhi on November 10, 2025.
About Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is a small, circular genome located within the cell's mitochondria, distinct from the large linear chromosomes in the nucleus. It is crucial for energy production and is almost exclusively maternally inherited.
Structure and Function
- Location: Resides in the mitochondria, the "powerhouses" of the cell responsible for converting chemical energy from food into adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
- Structure: Unlike nuclear DNA (nDNA), mtDNA is typically a double-stranded, closed circular molecule and lacks protective histone proteins, making it more susceptible to damage from reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced during energy metabolism.
- Size and Genes: In humans, it is small, containing 16,569 base pairs and 37 genes in total. These genes encode 13 proteins essential for the oxidative phosphorylation system, 22 transfer RNAs (tRNAs), and two ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), all necessary for protein synthesis within the mitochondria.
- Origin: The presence of mtDNA supports the endosymbiotic theory, which posits that mitochondria were once free-living bacteria that were engulfed by ancestral eukaryotic cells nearly two billion years ago, forming a symbiotic relationship.
Key Characteristics of mtDNA Inheritance
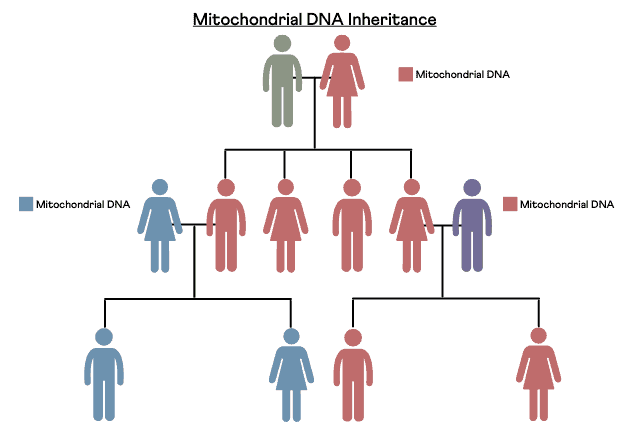
- Maternal Inheritance: mtDNA is passed down intact from a mother to all of her offspring (sons and daughters).
- No Recombination: Unlike nuclear DNA, mtDNA does not undergo recombination, meaning it remains relatively unchanged over generations, with only occasional mutations. This makes it a clear, unbroken line for tracing direct maternal ancestry.
- Tracing Limitations: While both men and women can take the test, only women can pass on their mtDNA to the next generation. Therefore, the test only provides information about the single, direct maternal line (mother's mother's mother, etc.) and not all female ancestors.
- Variability: Since the mutation rate is slow, a perfect mtDNA match may be a recent cousin or a relative from hundreds or thousands of years ago.
Role in Disease and Medicine
- Mutations in mtDNA can lead to a range of inherited and age-related disorders, often affecting tissues with high energy demands like the brain, heart, and muscles.
Examples of related conditions include:
- Leber hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON), which causes vision loss.
- MELAS (mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes).
- Kearns-Sayre syndrome (KSS), associated with muscle weakness and cardiac issues.
mtDNA analysis is also a valuable tool in forensics, particularly for identifying human remains when nuclear DNA is degraded (e.g., in ancient bones or hair samples), due to its high copy number per cell.
Mitochondrial DNA test
A mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) test analyzes the DNA found in a cell's mitochondria to trace an individual's direct maternal lineage or screen for mitochondrial diseases. Unlike nuclear DNA, which is a mix of both parents, mtDNA is inherited exclusively from the mother by all her children, but only females pass it on to the next generation.
Applications of Mitochondrial DNA Testing
Mitochondrial DNA testing is used in several fields:
- Genealogy and Ancestry: This is a primary use of mtDNA testing. By tracking the mutations (polymorphisms) in a person's mtDNA and comparing them to databases, the test can trace their maternal ancestry back thousands of years and link them to a specific maternal haplogroup (a major branch of the human family tree). It helps find genetic relatives who share a common maternal ancestor.
- Forensic Science: In cases involving severely degraded biological evidence like old bones, teeth, or hair shafts, where nuclear DNA might be insufficient, the high copy number of mtDNA in each cell makes analysis possible. It can be used for human identification, such as identifying unidentified human remains or war casualties, by comparing the results with potential maternal relatives.
- Clinical Diagnostics and Disease Research: Mutations in mtDNA can cause a wide range of inherited conditions known as mitochondrial diseases. Testing can help diagnose these disorders, which may affect multiple bodily systems and present with varied symptoms, from exercise intolerance to diabetes and deafness. It is a powerful tool when nuclear DNA testing results are negative but a mitochondrial condition is still suspected.
- Legal Matters: A legal mtDNA test can provide scientific evidence for inheritance disputes or other legal cases that require confirmation of a biological maternal relationship.
National Database for Emergency Management
The latest news regarding India's National Database for Emergency Management (NDEM) includes the mandatory use of its datasets for all highway project reports and the recent launch of new technological platforms that utilize the database.
About National Database for Emergency Management
The National Database for Emergency Management (NDEM) is a comprehensive geospatial platform developed by ISRO and NRSC to support effective disaster risk reduction and emergency response in India.
Key Features
- NDEM is a unique geo-portal designed for dissemination of space-based data and services from forecasting organizations, addressing all major natural disasters in India.
- It is a centralized, national repository of multi-scale geospatial databases, integrated with customized decision support system tools for disaster management authorities and officials.
- The portal is maintained by the National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC) under ISRO, with the guidance of the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA).
Objectives
- To synergize disaster-related data and near real-time alerts from multiple forecasting organizations on a single national platform.
- To provide timely information and disaster-specific products for preparedness, hazard/risk zonation, damage assessment, and emergency response.
- To strengthen decision-making processes for all States/UTs, NDRF/SDRF, and other disaster management agencies.
Technical and Operational Details
- NDEM offers multi-temporal satellite imagery, thematic layers, and hazard maps for floods, earthquakes, landslides, droughts, cyclones, and forest fires.
- The portal provides decision support tools including routing, proximity analysis for emergency facilities, geospatial visualization, and historical data queries for disaster events.
- A mobile version (NDEM Lite 2.0) allows ground-level officials to access alerts and updates in near real-time for operational efficiency during emergencies.
Usage and Implementation
- As of 2025, the Ministry of Road Transport has mandated the integration of NDEM analysis in all highway project reports to ensure disaster resilience in infrastructure.
- Regular capacity-building initiatives, trainings, and mock drills are conducted for state and central disaster management officials to maximize the use and impact of NDEM services.
Institutional Support
- NDEM aids in planning, management, and mitigation for a range of hazards in India, making it an essential tool in the national disaster management strategy.
- It provides access to live and historical disaster alerts, as well as integrated services for analysis, visualization, and on-ground support to disaster response forces.
This structured approach supports proactive and informed action for emergencies and enables a technology-driven, resilient disaster management ecosystem in India.
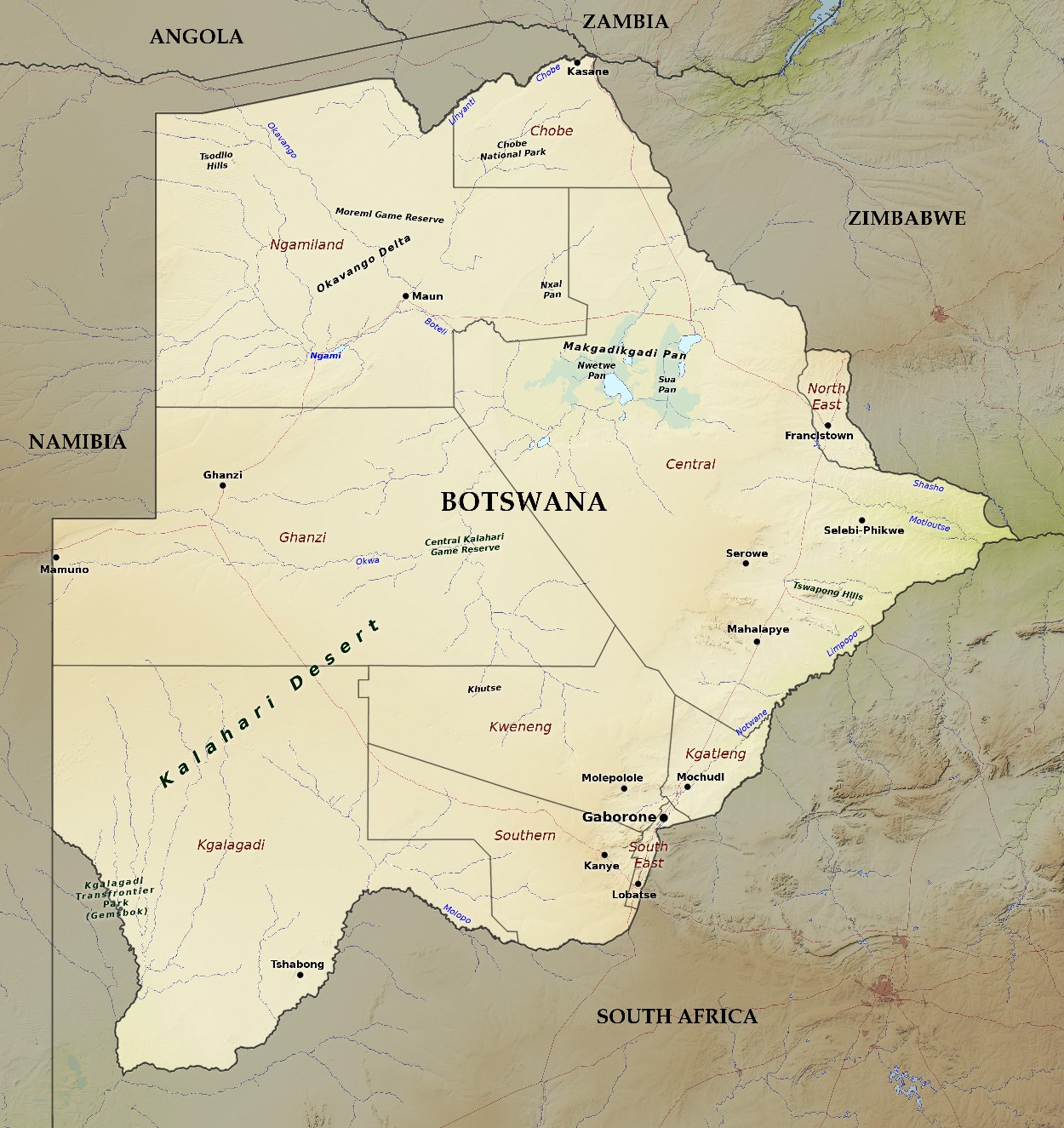
Recently, India and Botswana formally announced the translocation of eight Cheetahs from the African nation during the State visit of the President of India.
About Botswana
Botswana is a landlocked country in Southern Africa known for its stable democracy, successful economy driven by diamond mining, and diverse geography that includes the Kalahari Desert and the Okavango Delta. The nation's culture is deeply influenced by the Batswana people and the concept of Botho, an emphasis on community and respect.
Facts at a glance
| Statistic |
Value |
| Capital |
Gaborone |
| Population |
2,521,139 (as of 2024) |
| Official Language |
English and Setswana |
| Currency |
Pula (BWP) |
| Area |
581,730 sq km |
| Government |
Parliamentary Republic |
| Gained Independence |
September 30, 1966 |
Geographical features of Botswana
- Location: Botswana is a landlocked country in Southern Africa, bordered by Namibia, South Africa, Zimbabwe, and Zambia. It occupies an area of about 581,730 square kilometers.
- Terrain: The country is predominantly flat to gently undulating tableland with few hills. It forms part of the Kalahari Basin with an average altitude of around 1000 meters above sea level.
- Kalahari Desert: Covering about 70% of the country, the Kalahari Desert is a semi-desert or bush savannah rather than a true desert, characterized by sandy terrain and sparse vegetation.
- Okavango Delta: Located in the northwest, it is the world's largest inland delta, rich in biodiversity with a network of water channels, lagoons, swamps, and islands.
- Makgadikgadi Pans: Large salt pans in the north-central part of Botswana, remnants of a prehistoric lake that evaporated, leaving extensive salt flats and seasonal wetlands.
- Natural regions: Botswana has three main geographic regions:
- Hardveld Region - rocky hills and shallow sand cover in the east.
- Sandveld Region - deep Kalahari sands covering most of the rest of the country.
- Ancient lake beds - found in the northern sandveld within the Kalahari Basin.
- Rivers: The main rivers include the Okavango, Chobe, Limpopo, and Molopo. The Okavango River forms the delta but does not flow to the sea (endorheic basin).
- Elevation: The highest point is Monalanong Hill at about 1,495 meters, and the lowest point is at the junction of the Limpopo and Shashe Rivers at 513 meters elevation.
- Climate: Semi-arid with warm winters and hot summers, the country experiences high sunshine all year round and has a dry, windy, and dusty season.
- Vegetation: Ranges from semi-desert bush savannah in the Kalahari area to tree savannah around the Okavango Delta and more densely vegetated areas along rivers.
- Human Settlement: Most of the population is concentrated in the eastern region, where the terrain is less arid and more varied.
Metformin
Recent news regarding Metformin ((1,1-dimethylbiguanide hydrochloride focuses on its potential benefits beyond diabetes management, particularly in reducing the risk of long COVID-19, new insights into its mechanism of action (including a brain pathway), and a study suggesting it may blunt the benefits of exercise in some areas.
About Metformin
Metformin is a widely used oral medication for managing type 2 diabetes, particularly in individuals who are overweight or obese. It helps the body use its own insulin more effectively and lowers blood sugar levels. It is also prescribed "off-label" for other conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS).
How Metformin Works
Metformin is the only drug in the biguanide class available today. It primarily lowers blood sugar through several mechanisms:
- Decreasing glucose production in the liver.
- Increasing the body's sensitivity to insulin, which helps body cells absorb more glucose from the blood.
- Slowing the absorption of glucose from the food you eat in the intestines.
It usually does not cause hypoglycemia (abnormally low blood sugar) when taken alone, a benefit over some other diabetes medications.
Common Uses
The primary use of metformin is for type 2 diabetes management, but healthcare providers may prescribe it for other conditions as well:
- Type 2 Diabetes: First-line treatment to manage blood glucose levels when diet and exercise are insufficient.
- Prediabetes: May be prescribed to help prevent or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes in high-risk individuals.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): Used off-label to help regulate menstrual cycles, improve ovulation, and manage insulin resistance.
- Gestational Diabetes: Sometimes used to control blood sugar during pregnancy.
Side Effects
Metformin is generally well-tolerated, but side effects can occur. They often improve over the first few weeks of treatment.
- Common Side Effects: Gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, gas, stomach pain, and a metallic taste in the mouth.
Serious (but Rare) Side Effects:
- Lactic Acidosis: A dangerous buildup of lactic acid in the blood. Symptoms can include unusual muscle pain, trouble breathing, stomach pain, dizziness, feeling cold, or feeling very weak or tired. This risk is higher in people with kidney or liver disease, severe infection, or those who consume excessive alcohol.
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Long-term use can lead to lower levels of vitamin B12, so doctors may monitor levels and recommend supplements.
- Allergic Reactions: Seek emergency help if you experience hives, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat.
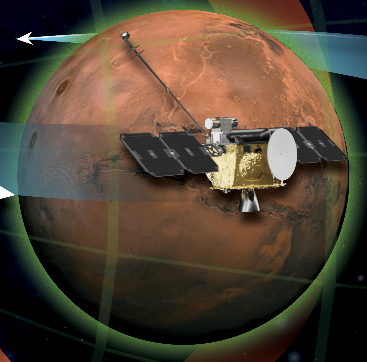
Recently, Blue Origin has successfully launched Nasa’s highly anticipated Escapade mission to Mars.
About ESCAPEDE Mission
The ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) mission is NASA's latest multi-spacecraft science mission to Mars, featuring two orbiters named Blue and Gold. Its primary goal is to investigate how the solar wind interacts with the Martian magnetic field and how this contributes to atmospheric loss on Mars—a key question in understanding the planet's evolution and habitability.
Mission Highlights
- ESCAPADE is the first mission to use two simultaneous orbiters around Mars, allowing for coordinated multi-point observations of the planet’s space weather and magnetospheric environment.
- Launched on November 13, 2025, aboard Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket, the spacecraft will spend up to a year in Earth orbit before heading to Mars, with arrival expected by 2027.
- Once at Mars, the two orbiters will fly in tandem but take slightly different orbits to maximize spatial coverage, providing complementary scientific data through at least 2029.
Scientific Objectives
- Understand the processes structuring Mars’ hybrid magnetosphere and how it guides ion and plasma flows.
- Analyze how energy and momentum are transported from the solar wind through the Martian magnetosphere to the atmosphere.
- Investigate how matter and energy flow into and out of Mars' upper atmosphere—key drivers of atmospheric escape, which relates to how Mars lost most of its original atmosphere and water over billions of years.
Unique Mission Features
- ESCAPADE's twin orbiters will provide, for the first time, simultaneous measurements from different locations around Mars, offering a detailed real-time picture of how space weather impacts the planet.
- The mission uses an innovative launch profile: after initial launch, the spacecraft will loop around a space region near the Earth-Sun L2 point and wait for optimal Mars transfer conditions, then use an Earth gravity assist to sling themselves toward the Red Planet.
- This mission is part of NASA’s SIMPLEx program, emphasizing innovative, lower-cost planetary exploration.
ESCAPADE’s results are expected to fill critical gaps in Mars atmospheric and magnetospheric science, helping protect future human explorers from space weather hazards and shedding light on the Red Planet’s dramatic climate changes.
India's Hydrogen Valley Innovation Clusters (HVICs)
The most recent news (November 2025) concerns India's official launch of four national Hydrogen Valley Innovation Clusters (HVICs) with a total investment of ?485 crore to demonstrate the entire green hydrogen value chain.
Key Developments
- Four HVICs Established: India is setting up four "living laboratories" across the country to showcase large-scale hydrogen production, storage, transport, and utilization. These clusters are designed to accelerate the clean energy transition, foster innovation, and develop standards and policies for the hydrogen economy.
- Significant Investment: The initiative involves a total investment of approximately ?485 crore (around $58 million USD), with ?169.89 crore from the National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM) and the remainder from industry partners.
- Integration under NGHM: The HVICs, initially conceptualized by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), have been integrated into the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy's (MNRE) National Green Hydrogen Mission.
- Funding Approvals: In July 2025, the MNRE approved $7.8 million in funding for four specific HVIC projects, including a project in Pune receiving $2 million and plans for Kerala receiving $2.4 million.
- Ports Designated as Green Hydrogen Hubs: In October 2025, three major ports—Deendayal Port (Gujarat), V.O. Chidambaranar Port (Tamil Nadu), and Paradip Port Odisha)—were formally recognized as Green Hydrogen Hubs. This move, operating under revised June 2025 guidelines, supports a cluster-based development model for project viability and scale.
Project Locations and Partners
Specific projects are being developed in collaboration with various entities:
- Pune, Maharashtra: A project is led by the National Chemical Laboratory (CSIR-NCL).
- Kerala: The state government has given its nod to the HVIC-Kerala, a not-for-profit company led by the Agency for New and Renewable Energy Research and Technology (ANERT) to implement the project.
- Tamil Nadu: IIT Madras is working with industries, including a collaboration with Hyundai, to establish an innovation hub and develop indigenous technologies.
The goal of these HVICs is to create a robust domestic supply chain and position India as a global leader in green hydrogen production and export by 2030.
What is Green Hydrogen?
Green Hydrogen is hydrogen produced through the electrolysis of water using electricity generated from renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, or hydropower, making its production carbon-neutral and environmentally friendly.
Green Hydrogen
- It is hydrogen gas generated by splitting water (H2O) into hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) through a process called electrolysis.
- The electricity used in electrolysis is sourced entirely from renewable energy, so the process emits no greenhouse gases.
- It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible fuel.
- Green hydrogen production avoids carbon dioxide emissions unlike "grey hydrogen" (produced from fossil fuels without carbon capture) and "blue hydrogen" (fossil fuel-based but with carbon capture).
- It is considered a zero-emission fuel and plays a crucial role in decarbonizing industries, heavy transport, and power generation sectors.
- Hydrogen produced in this way can be stored and used to stabilize energy supply from intermittent renewable power sources.
- Its applications include use in heavy industries (steel, chemicals, ammonia), transportation (ships, trucks, trains, airplanes), and long-term energy storage.
- The byproduct oxygen from electrolysis can also be used commercially for industrial and medical purposes.
- Countries with renewable energy abundance, like India with its National Green Hydrogen Mission, aim to increase production capacity and utilize green hydrogen for energy independence and emissions targets.
- It has the potential to replace fossil fuels in many sectors, helping reduce dependency on imports and significantly cutting greenhouse gas emissions.
Thus, green hydrogen represents a key element in the transition to clean, sustainable energy systems aimed at mitigating climate change and achieving net-zero carbon goals.
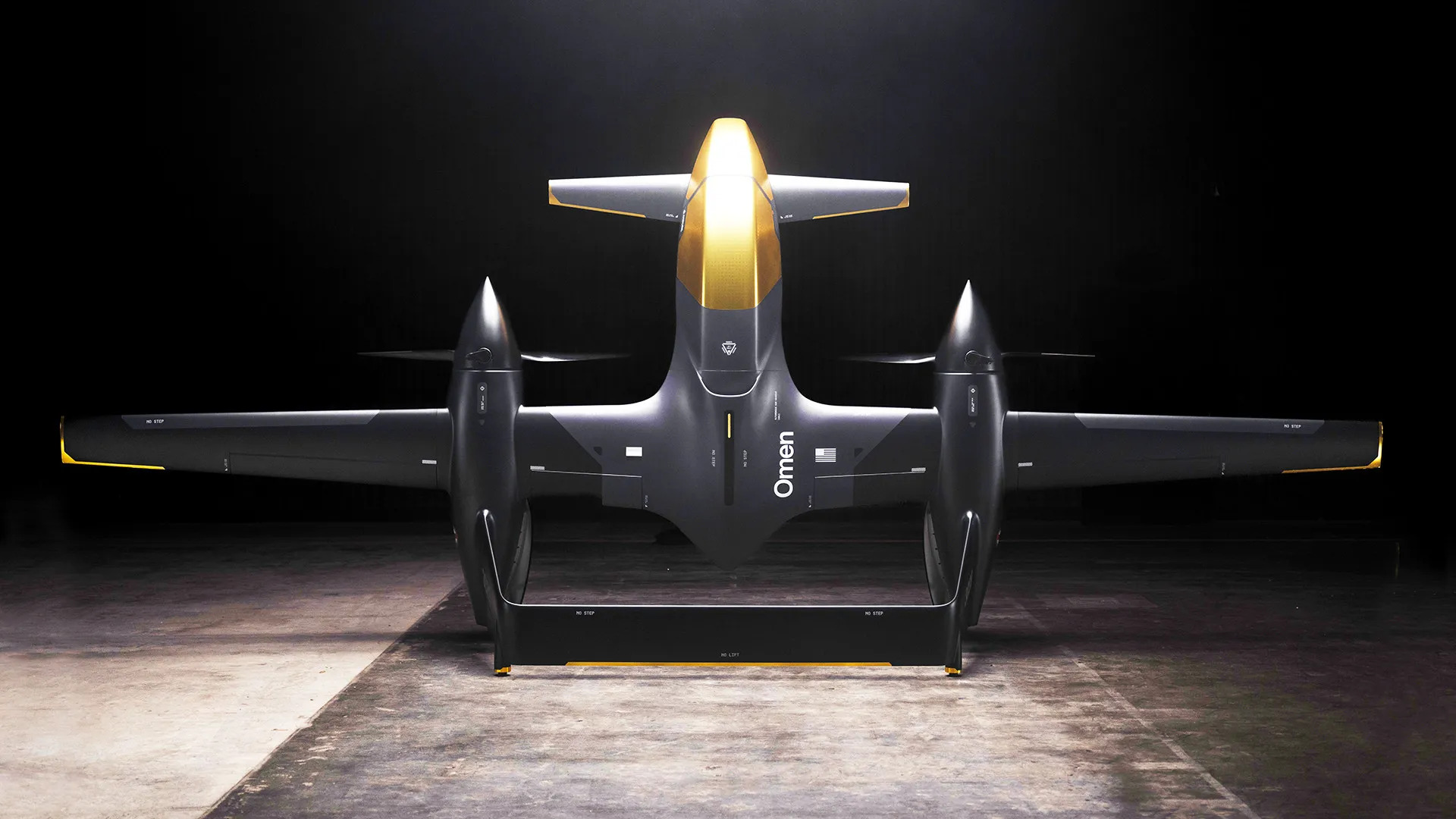
The latest news regarding the Omen drone is that the US defense tech firm Anduril and the UAE's state-owned defense conglomerate EDGE Group have formed a joint venture to co-develop and manufacture the AI-powered drone in the United Arab Emirates.
Omen drone based on the latest information:
- The Omen drone is a tail-sitting vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) unmanned aerial system (UAS), developed by Anduril in partnership with the EDGE Group in the UAE.
- It belongs to the U.S. military's Group 3 drone category, which includes drones weighing between 55 and 1,320 pounds, capable of flying at altitudes between 3,500 and 18,000 feet, with top speeds from 100 to 250 knots (around 115-290 mph).
- The drone is about 3 meters (10 feet) tall standing in its tail-sitting position, with long slender wings and canard foreplanes, and a twin-boom tail design.
- The propulsion system is hybrid-electric: a gasoline-powered generator charges onboard batteries that power electric propulsors. This gives Omen extended flight endurance and the ability to hover for intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) tasks, while also enabling faster dash speeds compared to pure battery-electric drones.
- It can switch between two flight modes: hover like a helicopter or drone, and airplane-style forward flight for longer endurance and higher speed missions.
- The Omen drone carries three to five times the payload of typical Group 3 drones, which usually carry 25 to 50 pounds. This enables carrying multiple sensors like synthetic aperture radar (SAR), electro-optical (EO) sensors, electronic warfare payloads, and potentially munitions.
- It is designed for modularity and an open-architecture system allowing integration of diverse payloads for military missions like maritime patrol, air defense sensing, communication relay, and logistics, as well as civilian missions such as disaster relief, search and rescue, and communication restoration.
- Omen has a foldable frame for easy transport and deployment by a two-person team without specialized infrastructure, allowing rapid launch from remote or austere locations including forest clearings, rooftops, or naval vessels.
- Its endurance is said to be three to four times greater than current Group 3 drones, with operational ranges suitable for remote mission theaters such as the Indo-Pacific region.
- The drone can operate in coordinated swarms using Anduril’s Lattice AI autonomy software, which enables real-time data sharing, route adaptation, and complex swarm behaviors for extended sensor coverage.
- The initial production and assembly facility is in Abu Dhabi, with a first order of 50 units for UAE forces, emphasizing local production and supply chains.
This makes the Omen a versatile, powerful, hybrid-electric VTOL drone with enhanced endurance, payload, and modularity to serve across military and civilian applications.
The Ministry of Defence recently inked an agreement with Bharat Dynamics Limited for the procurement of INVAR Anti-Tank Missiles worth over 2 thousand 95 crore rupees to enhance the lethality of T-90 tanks.
About INVAR Missile
- The INVAR missile is a sophisticated laser-guided anti-tank guided missile (ATGM) designed to be launched from the 125mm smoothbore gun barrel of main battle tanks, especially the T-90 tank, which is a key asset of the Indian Army's armored regiments.
- It has a high hit probability and precision strike capability, capable of destroying stationary and moving armored targets, including those equipped with Explosive Reactive Armor (ERA).
- The missile is originally developed by Russia's Rosoboronexport and is produced under license in India by Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL).
Key features of the INVAR missile include:
- Semi-automatic laser beam riding guidance that is immune to jamming.
- A tandem warhead designed to penetrate modern tank armors.
- Maximum range of approximately 5 kilometers with a flight time of about 17.6 seconds.
- Ability to destroy targets moving up to 70 km/h.
- Weight around 17.2 kg with a caliber of 125 mm.
- It enhances the lethality and firepower of T-90 tanks, significantly improving mechanized operations and operational advantage against adversaries.
Recently, the Indian Ministry of Defence signed a contract worth ?2,095.70 crore with Bharat Dynamics Limited for the procurement of 500 INVAR missiles to equip the T-90 tanks, highlighting a major upgrade in the Indian Army's armored warfare capabilities and supporting the goal of Aatmanirbharta (self-reliance) in defense production.
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
Recently, a report explains how experts use the Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) to analyse post-blast forensic investigations.
About Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy is an analytical technique used to obtain an infrared spectrum of the absorption or emission of a solid, liquid, or gas to identify its chemical composition. It works by measuring how molecules absorb infrared light at specific frequencies, which correspond to the vibrational modes of their chemical bonds, producing a unique "molecular fingerprint".
Principle of Operation
The core component of an FTIR spectrometer is a Michelson interferometer, which uses a beam splitter, a fixed mirror, and a moving mirror to modulate the infrared light beam. This process simultaneously collects information from all infrared frequencies.
- Source: A broadband infrared light source emits a beam of radiation.
- Interferometer: The beam enters the Michelson interferometer, where the beam splitter divides it into two paths. One beam goes to a stationary mirror, and the other to a mirror that moves back and forth. The beams reflect and recombine at the beam splitter, creating an interference pattern called an interferogram.
- Sample: The recombined beam passes through or reflects off the sample, which absorbs specific frequencies of light characteristic of its molecular structure.
- Detector: The detector measures the intensity of the light after interacting with the sample, producing a raw signal (interferogram) that is a function of the mirror's position (or time).
- Computer: A mathematical process called a Fourier transform converts the interferogram from the time/spatial domain into an interpretable spectrum (intensity versus frequency, typically in wavenumbers, cm¹).
Advantages over Dispersive IR
FTIR has largely replaced older dispersive IR spectrometers due to several key advantages:
- Speed (Fellgett's Advantage): It measures all infrared frequencies simultaneously, providing significantly faster scan times.
- Sensitivity (Jacquinot's Advantage): It has higher optical throughput (allows more light to pass through) because it uses an aperture instead of narrow slits, resulting in a better signal-to-noise ratio.
- Accuracy (Connes's Advantage): A built-in laser (e.g., Helium-Neon) is used to calibrate the wavelength scale precisely with each scan, providing high wavenumber accuracy.
- Versatility: A wide range of sampling techniques (transmission, attenuated total reflectance (ATR), reflectance) allow analysis of solids, liquids, gases, powders, and pastes with minimal or no sample preparation.
Common Applications
FTIR is a versatile tool used across many industries and research fields:
- Chemical Analysis: Identifying and characterizing organic and some inorganic compounds based on their functional groups and molecular structure.
- Quality Control: Verifying raw materials, ensuring batch consistency in manufacturing, and detecting impurities or contaminants.
- Materials Science: Analyzing polymers, coatings, and composites to understand their composition and properties.
- Forensics: Identifying trace evidence, unknown substances, and illicit narcotics.
- Biomedical & Pharmaceutical: Studying protein structures, analyzing tissues and cells for disease detection (e.g., cancer diagnostics), and ensuring drug quality.
- Environmental Monitoring: Detecting pollutants and analyzing microplastics in environmental samples.
Penganga River
Four women and three children trapped for almost two hours in the gushing water of the Penganga River, near the famous Sahastrakund waterfall, were rescued recently.
About Penganga River
The Penganga River (also known as the Painganga) is a major river in the Maharashtra state of India and a chief tributary of the Wardha River. It eventually flows into the Godavari River basin.
Key Features
- Origin: The Penganga originates in the Ajanta ranges (Ajantha Hills) in the Buldhana district of Maharashtra.
- Course: It flows generally in a southeastern direction, traversing and forming natural boundaries between several districts including Buldhana, Hingoli, Nanded, Yavatmal, Washim, and Chandrapur. It also acts as an inter-state border between Maharashtra and Telangana.
- Length: The total length of the river is approximately 676 km (420 miles).
- Confluence: It merges with the Wardha River near Wadha village in the Chandrapur district. The combined flow of the Wardha and Wainganga rivers forms the Pranahita River, which is the largest tributary of the Godavari River.
- Tributaries: The main tributaries of the Penganga are the Adan, Kas, Arunavati, Kayadhu, and Pus rivers.
Significance and Projects
Irrigation: The river is a vital source of water for domestic and irrigation use, benefiting the Yavatmal, Hingoli, and Nanded districts of Maharashtra.
Dams and Projects:
- The Upper Painganga Dam, also known as the Isapur Dam, is a major earthfill dam on the river that provides significant irrigation potential.
- The Lower Penganga Project is another major inter-state irrigation project with Telangana (formerly Andhra Pradesh) to utilize the river's water for irrigation in both states.
- Construction of barrages, such as the Korata-Chanaka barrage, is also part of ongoing efforts for water management and flood control.
Ecology: A protected forest area known as the Painganga Wildlife Sanctuary is situated along both banks of the river, covering parts of the Yavatmal and Nanded districts. The river is also known for the scenic Sahastrakund Waterfall.
Navigation: The river is generally deeply entrenched and difficult to navigate, with flooding common during the monsoon season.
Mission Sudarshan Chakra is India's ambitious, indigenous, and multi-layered national security initiative aimed at creating a comprehensive defence shield by 2035. Announced by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in August 2025, the mission is designed to protect critical military and civilian infrastructure from various threats, including missiles, drones, and cyber attacks.
Modelled partly on Israel's "Iron Dome," the system is intended to provide both defensive and offensive capabilities, ensuring a robust response to enemy aggression.
Key Features and Objectives
- Multi-Layered Defence: The mission will integrate an overlapping network of early-warning and tracking sensors, command and control posts, and land/sea-based interceptor missiles.
- Indigenous Technology: A core principle is the complete indigenization of research, development, and manufacturing of the entire system, aligning with the Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- Integrated Systems: It will combine surveillance, cybersecurity, and air defence, linking existing systems like the Air Force's Integrated Air Command and Control System (IACCS) and the Army's Akashteer network.
- Comprehensive Protection: The security cover will extend to all critical and strategic locations, including sensitive defence facilities, nuclear installations, hospitals, railway hubs, and religious centers.
- Precision Strike Capability: Inspired by the mythological Sudarshan Chakra of Lord Krishna, the system aims to neutralise threats and enable swift, precise counter-strikes.
- Future Technologies: The plan includes integrating advanced technologies such as space assets (satellites), directed-energy weapons (DEWs), and AI algorithms for rapid target selection.
The project, spearheaded by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and involving private industry partners, represents a significant leap in India's national security infrastructure, aiming for self-reliance and strategic autonomy in the defence sector by the target year of 2035.
Download Pdf