CA-15/09/2025
Operation polo
Why in News?
Operation Polo marks the 77th anniversary of the historic military action launched by India on 13th September 1948 to annex the princely state of Hyderabad.
Major highlights of Operation Polo:
Background and Causes
- Refusal to Accede: After India's independence, all princely states were given the choice to join India or Pakistan. The Nizam of Hyderabad, with a majority Hindu population but a Muslim ruling elite, sought to maintain Hyderabad as an independent nation.
- Strategic Location: Hyderabad was a large, landlocked state situated in the heart of India. Its independence was seen as a major threat to India's territorial integrity and a potential "cancer in the belly of India," as described by Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel.
- Rise of the Razakars: A private, radical Muslim militia known as the Razakars, led by Qasim Razvi, gained immense power and influence. They committed widespread violence and atrocities against those who supported accession to India.
- Standstill Agreement and Escalation: A standstill agreement was signed between Hyderabad and India in November 1947, but this period was used by the Nizam to import arms (reportedly from Pakistan) and strengthen his military, while the Razakars intensified their violent activities.
About Operation
- Code Name: The operation was officially termed a "police action" to avoid the international perception of it being an act of war.
- Swift and Decisive Action: On September 13, 1948. The Indian forces, led by Major General J.N. Chaudhuri remarkably overpowered the Nizam's army and the Razakars only in five days.
- Nizam's Surrender: Faced with imminent defeat, the Nizam, Mir Osman Ali Khan, formally surrendered and signed the Instrument of Accession, integrating Hyderabad into the Indian Union.
Outcomes and Aftermath
- Hyderabad was placed under military administration until December 1949.
- Later, a civilian government was appointed by the Ministry of States.
- Elections were conducted in 1952, marking the democratic transition of Hyderabad into the Indian Union.
- Reorganization of the State: Hyderabad was later reorganized on a linguistic basis in 1956, with its different parts becoming part of the new states of Andhra Pradesh (now Telangana and Andhra Pradesh), Maharashtra, and Karnataka.
- Commemoration: September 17 is often marked as "Hyderabad Liberation Day" to commemorate the day the state was freed from the Nizam's rule and joined the Indian Union.
Manki-Munda
Why in news?
Recently, there have been protests and rallies by the Ho tribe community in Jharkhand against alleged administrative interference and attempts to reform or interfere with this traditional governance system.
About Manki-Munda
- The Manki-Munda system is a centuries-old traditional self-governance framework of the Ho tribal community in Jharkhand’s Kolhan region.
- Traditional Governance: It's a centuries-old, decentralized system of administration and justice.
Hierarchical Structure:
- Munda: The head of a single village. The Munda is responsible for resolving socio-political disputes at the local level. This is a hereditary position.
- Manki: The head of a "pir," which is a cluster of 8 to 15 villages. The Manki handles cases that cannot be resolved by the Munda. This is also a hereditary post.
Role in Community:
- The system is based on customary laws and plays a crucial role in maintaining social order, protecting cultural identity, and managing local affairs.
- Historically, before British rule, the system was purely for internal governance and did not involve revenue collection or land taxation.
British Influence:
- After early revolts by the Ho and Kol tribes, the British codified the Manki-Munda system in 1837 with the "Wilkinson's Rules."
- This British intervention integrated the Mankis and Mundas into the colonial administration, making them intermediaries for collecting revenue and reporting to the British authorities.
Post-Independence:
- The system has largely continued to operate in the Kolhan region, with courts often recognizing it as a valid form of customary practice.
- However, its relevance has been challenged by the modern Panchayati Raj system and by a younger generation that sometimes calls for reforms to the hereditary nature of the posts.
Recent tensions have risen because of vacant leadership posts, complaints about some Mundas not performing their duties, and demands for reforms to allow more educated and competent leadership instead of purely hereditary appointments.
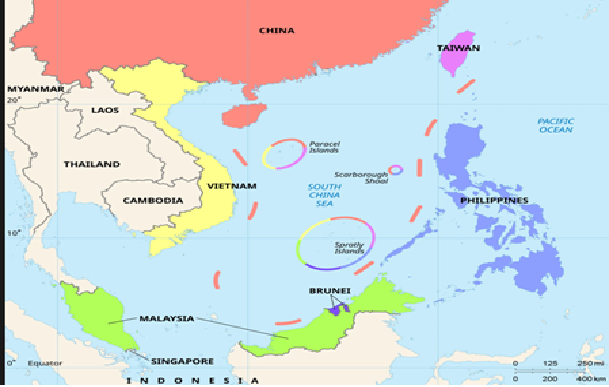
Scarborough Shoal
Why in news?
Recently, China announced the establishment of a "National Nature Reserve" at Scarborough Shoal, a move it says is intended to protect the marine ecosystem.
About Scarborough Shoal
- Scarborough Shoal is a small, triangular-shaped coral atoll located in the South China Sea. It is also known by other names, including Huangyan Island (China) and Bajo de Masinloc or Panatag Shoal (Philippines).
Geography
- Location: Scarborough Shoal is situated approximately 220 km (120 nautical miles) west of the Philippines' main island of Luzon. It is located far closer to the Philippines than to the nearest major Chinese landmass, which is over 800 km away.
- Physical Features: The atoll has a circumference of about 46 km and an area of 150 square km, which includes a shallow, navigable lagoon.
Historical Context
- Named after the British merchant ship Scarborough which ran aground there in 1748.
- The area has been known by various names historically, including Maroona Shoal (Spanish era map).
Territorial Dispute
- Claimed by the Philippines, China, and Taiwan.
- China bases its claim on a historical narrative, stating that it has had ancestral territory in the region since the Yuan dynasty in the 13th century and secondly its part of broader claim to nearly the entire South China Sea, which is demarcated by what is known as the "nine-dash line."
- Philippines' claim is based on its geographical proximity and the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), under which the shoal lies within its 200-nautical-mile exclusive economic zone (EEZ).
- The 2012 Scarborough Shoal standoff saw China take effective control after blocking Philippine attempts to detain Chinese fishermen.
- The United Nations Permanent Court of Arbitration ruled in 2016 that China's expansive claims based on the "nine-dash line" have no legal basis, a verdict China rejects.
- China's presence has increased with coast guard patrols limiting Filipino fishermen’s access.
Strategic Importance
- Located near vital shipping lanes carrying over $3 trillion worth of global trade annually.
- Provides a natural safe harbor during storms for fishing vessels.
- The shoal's control offers strategic military and navigation advantages for regional powers.
Environmental and Economic Significance
- The surrounding waters are rich fishing grounds sustaining thousands of livelihoods, especially for Filipino coastal communities.
- Coral reef ecosystems are abundant, warranting environmental conservation efforts by claimant states.
The Scarborough Shoal dispute is emblematic of broader tensions between China and Southeast Asian nations over sovereignty, maritime rights, and regional security in the South China Sea.
Digital arrest
Why in news?
Digital arrest scams have surged across country in recent months, with daily headlines reporting large financial losses, arrests, and public outcry over banking lapses and law enforcement challenges.
What is Digital arrest?
- Digital arrest is a sophisticated cyber scam where fraudsters impersonate law enforcement or government officials to intimidate victims into transferring money, using psychological coercion and fake evidence.
Cases and Financial Losses
- In 2022, there were 39,925 reported digital arrest scam cases, and victims lost ?91.14 crore.
- By 2024, reported cases had tripled to 1,23,672, with losses soaring over ?1,935 crore—a 21-fold increase from 2022.
- Just in the first two months of 2025, 17,718 cases were reported, resulting in losses of ?210 crore.
- Bengaluru alone reported ?572 crore in losses over 18 months, with 1,004 registered cases between 2024 and mid-2025—accounting for 80% of Karnataka’s victims.
- Nationally, digital arrest scams are estimated to cost over ?2,000 crore ($240 million) annually.
Legal Provisions
While there are no specific laws for "digital arrest," the acts committed by the scammers fall under various provisions of law.
- Cheating: Scammers can be prosecuted for cheating by impersonation.
- Criminal Intimidation: The threats of arrest and legal consequences constitute criminal intimidation.
- Extortion: The act of demanding money through threats falls under extortion.
- Organized Crime: The BNS also has provisions to deal with organized crime syndicates involved in such cyber frauds.
- Identity Theft: Scammers are liable for identity theft and cheating by personation using a computer resource.
Government and Law Enforcement Response:
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C): This is a central body that coordinates efforts to combat cybercrime nationwide. It operates the National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal.
- National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal: The public can report all types of cybercrimes, including digital arrest scams, on this portal (cybercrime.gov.in) or by calling the helpline number 1930.
- Awareness Campaigns: The government and financial institutions like banks are running campaigns through various media channels to educate the public about these scams.
- Blocking of Accounts: Authorities are working with telecom providers to block SIM cards, Skype IDs, and WhatsApp accounts used for these fraudulent activities.
- Financial Fraud Reporting: The "Citizen Financial Cyber Fraud Reporting and Management System" helps in the immediate reporting of financial frauds to stop the siphoning of funds.
HIMARS missile
Why in news?
The U.S.A. is actively upgrading HIMARS with the next-generation Precision Strike Missile (PrSM), which extends the missile range up to 500 km and can hit moving targets, including ships at sea.
About HIMARS missile system
The HIMARS missile system (M142 High Mobility Artillery Rocket System) is a highly mobile, lightweight multiple rocket launcher developed by U.S.A. based Lockheed Martin for rapid deployment and precision strikes.
Key Features
- Mobility: HIMARS is mounted on a wheeled 5-ton Family of Medium Tactical Vehicles (FMTV), making it highly transportable by C-130 aircraft and suitable for fast relocation after firing.
- Armament: It carries either:Six Guided Multiple Launch Rocket System (GMLRS) rockets (range up to 80 km)and two Precision Strike Missiles (PrSM), Or one Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS) missile (range up to 300 km).
- Design: HIMARS features advanced fire control systems with GPS-guided targeting, enabling rapid aiming and firing missions in less than 20 seconds.
- Precision strikes against artillery, air defense, armored vehicles, and concentrated troops or supplies.
- Shoot-and-scoot tactics: The launcher can fire and quickly move away from the launch site, reducing vulnerability to counterattacks.
INS Androth
Why in news?
INS Androth is the second out of eight ASW-Shallow Water Crafts Built by Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers (GRSE), Kolkata is an indigenous Anti-Submarine Warfare Shallow Water Craft (ASW-SWC), was delivered to the Indian Navy on 13 September 2025.
Features & Capabilities
- The ship is named after Androth Island in the Lakshadweep archipelago.
- Length: Approximately 77.6 meters; Width: 10.5 meters; Draught: 2.7 meters.
- Displacement: 900 tonnes, gross tonnage 1,490 tonnes.
- The largest Indian Naval warship using diesel engine-waterjet propulsion.
- Indigenous content exceeds 80%, including equipment from Bharat Electronics, Mahindra Defence, and Larsen & Toubro.
- Designed for anti-submarine warfare in shallow littoral waters.
- Capable of full-scale sub-surface surveillance and anti-submarine operations.
- Enhances coastal surveillance and mine-laying capabilities.
Strategic Significance
- Represents a milestone in India’s indigenization and self-reliance (Aatmanirbhar Bharat) in naval defense manufacturing.
- Strengthens India’s ability to protect its vast maritime domain, especially in coastal and littoral zones.
- Enhances the Indian Navy’s preparedness against underwater threats, contributing to naval dominance in the Indian Ocean region.
INS Nistar
Why in news?
INS Nistar has participated in the multinational Exercise Pacific Reach 2025 in Singapore, engaging in submarine rescue exercises and expert exchanges with over 40 nations.
Key points about INS Nistar:
- India’s first indigenously designed and constructed Diving Support Vessel (DSV).
- The vessel serves as the "Mother Ship" for deep submergence rescue vessels to rescue personnel from distressed submarines underwater.
- Length: Approximately 118–120 meters
- Displacement: Over 10,000 tons
- Endurance: Over 60 days at sea
- Diving Depth: Saturation diving up to 300 meters, with additional shallow diving capability to 75 meters
- Equipped with state-of-the-art diving equipment such as Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs) capable of 1000 meters depth, self-propelled hyperbaric lifeboat, and diving compression chambers.
- High indigenous content of over 75-80%, involving participation from 120+ MSMEs, aligning with the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- Cost: Approximate project cost Rs 2,393 crore.
Strengthens India’s underwater warfare, maritime rescue, humanitarian assistance, disaster relief capacity, and deep-sea operational capability, also positioning India as a preferred submarine rescue partner in the region.
National Makhana Board
Why in news?
PM Modi officially launched National Makhana Board on September 14-15, 2025, in Purnea, Bihar as part of the Union Budget 2025-26 initiative.
Aims and objectives:
- Enhancing production standards and improving farming and post-harvest management techniques.
- Promoting value addition, innovative processing technologies, packaging, and branding.
- Expanding marketing networks and export linkages internationally.
- Providing financial assistance, training, and support to farmer-producer organizations to help them avail central government schemes.
- Developing infrastructure for advanced processing units, storage, and packaging facilities.
- Boosting the global reach of makhana as a superfood with nutritional and economic importance.
Economic Aspects
- Funding and Budget: The government allocated around Rs 100 crore for initial activities and a sizeable development package of nearly Rs 475 crore for the sector.
- Market Development: Supports branding, marketing, domestic and export market expansion, and integration of makhana farming with government schemes.
- Farmer Support: Focuses on organizing farmers into cooperatives and FPOs (Farmer Producer Organizations).
- Rural Employment: Boosts rural livelihoods by creating jobs, particularly empowering women in processing and allied sectors, and reducing seasonal migration.
- Export Potential: Makhana is recognized as a superfood with global demand expected to grow significantly. The Board aims to enhance export quality, expand global market share, and overcome infrastructure and export challenges.
Challenges
- Low Productivity: Traditional cultivation methods yield less, and there's limited adoption of modern techniques and high-yield varieties like 'Swarna Vaidehi'.
- Labor-Intensive Farming: Makhana cultivation is highly dependent on manual labor, which is physically draining and inefficient, with harvesting being particularly difficult and hazardous.
- Dominance of Intermediaries: A fragmented supply chain allows middlemen to exploit farmers by buying raw makhana at low prices, which reduces farmer profits.
- Lack of Awareness: Many farmers are not aware of available government schemes, subsidies, and modern agricultural practices that could help them improve their yield and income.
Download Pdf


Get in Touch